{
"cells": [
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"# Notebook 4: Pandas and visulization I."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"Here we will start using Pandas. Pandas is the standard way of working with tabular data. A great resource to learn more about Pandas is: http://pandas.pydata.org/"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Installation and downloads"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# downloading the example dataset that we'll use for this class. \n",
"# Pandas is already installed in colab by default as its very frequently used.\n",
"!pip -q install palmerpenguins"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
" \n",
"
\n",
"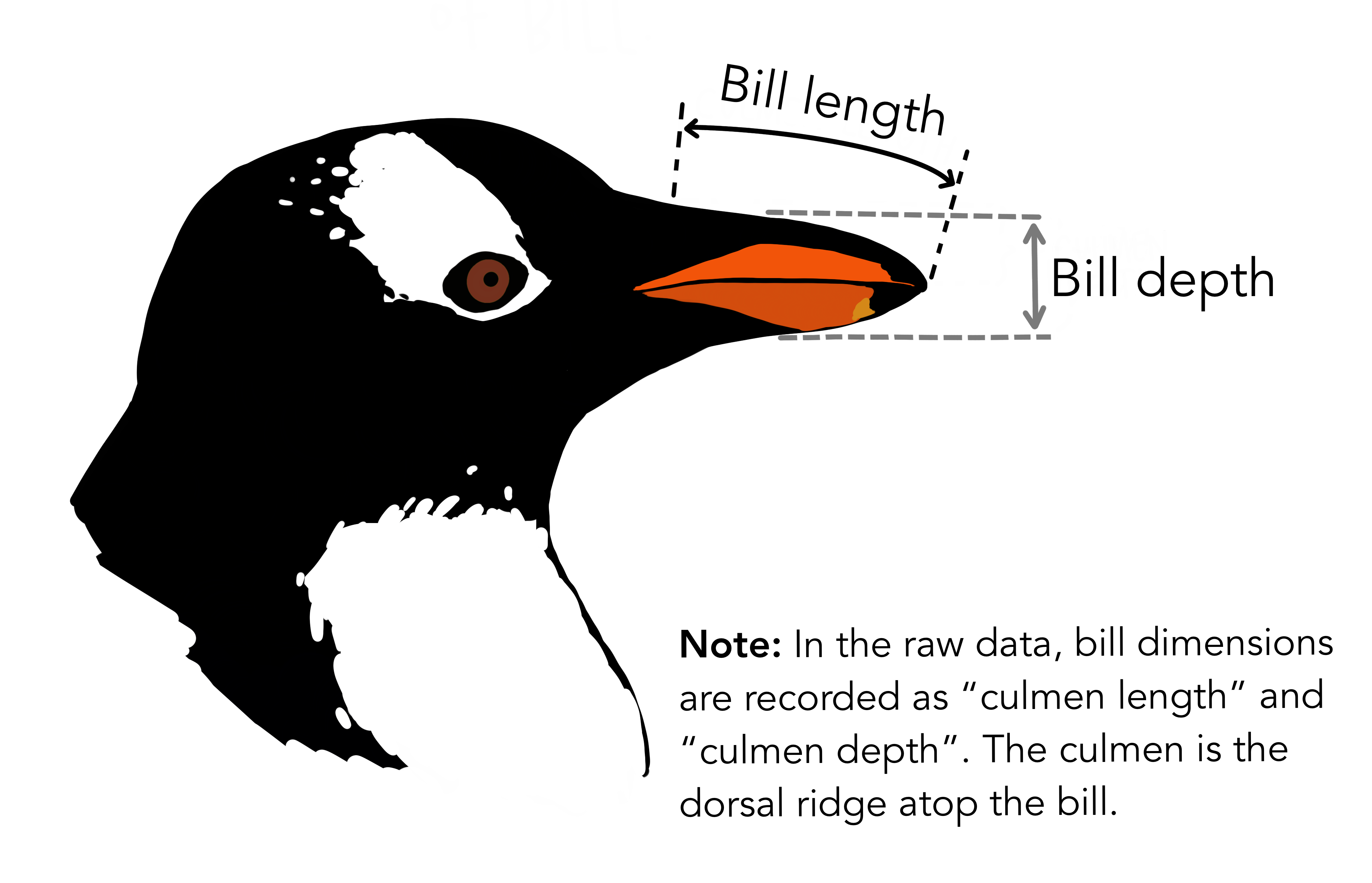 "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Introduction"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"Pandas is a library for working with tabular data. It was orignally based on the R data.frame library. \n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Loading and Displaying the Dataset\n",
"import pandas as pd\n",
"import seaborn as sns\n",
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
"import numpy as np\n",
"\n",
"from palmerpenguins import load_penguins\n",
"df = load_penguins()\n",
"\n",
"print(\"Type of the dataset:\", type(df))\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame using head command:\")\n",
"display(df.head())\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame using tail command:\")\n",
"display(df.tail())"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Key Concepts:\n",
"\n",
"- A DataFrame is a 2-dimensional data structure in pandas. It's like a spreadsheet or a table with rows and columns.\n",
"- Generally, \n",
" - Columns represent features (variables we measure or observe)\n",
" - Rows represent individual observations (in this case, each penguin)\n",
"\n",
"- In this dataset:\n",
" - Each row represents a single penguin\n",
" - Each column represents a feature (e.g., species, island, bill length)\n",
"\n",
"- Common functions for initial data exploration:\n",
" - df.head() Shows the first 5 rows by default\n",
" - df.info() Provides a concise summary of the DataFrame\n",
" - df.describe() Generates descriptive statistics for numerical columns"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Whole DataFrame Exploration\n",
"print(\"Summary statistics:\")\n",
"display(df.describe())\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nData types of columns:\")\n",
"display(df.dtypes)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nColumn names:\")\n",
"print(df.columns)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame info:\")\n",
"df.info()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Column Specific Operations\n",
"\n",
"# Using value counts to get the number of penguins for each species\n",
"species_counts = df['species'].value_counts()\n",
"print(\"Penguins per species:\")\n",
"print(species_counts)\n",
"\n",
"# Get the mean bill length\n",
"bill_length = df['bill_length_mm'].mean() # Can get the mode and sum\n",
"print(f'\\nAverage bill length: {bill_length}')\n",
"\n",
"# Get the mean bill length per species\n",
"species_bill_length = df.groupby('species')['bill_length_mm'].mean()\n",
"print(\"\\nAverage bill length per species:\")\n",
"print(species_bill_length)\n",
"\n",
"# Get the unique species\n",
"unique_species = df['species'].unique()\n",
"print(f\"\\nUnique species: {unique_species}\")\n",
"\n",
"# Get number of null values\n",
"boolean_vec = df.isnull()\n",
"print(f\"\\nBoolean_vec: {boolean_vec}\")\n",
"sum = boolean_vec.sum()\n",
"print(f\"\\nBoolean_vec sum: {sum}\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Data Cleaning\n",
"\n",
"# Examine original dataframe\n",
"print(\"Orifinal dataframe:\")\n",
"display(df)\n",
"\n",
"# Drop all rows with a null value\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe with non-null rows:\")\n",
"display(df.dropna())\n",
"\n",
"# Drop all columns with a null value\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe with non-null columns:\")\n",
"display(df.dropna(axis=1))\n",
"\n",
"# Replace all null values\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe with nulls replaced:\")\n",
"display(df.fillna(1))\n",
"\n",
"# Sort df based on column of interest\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe sorted based on column:\")\n",
"df_sorted = df.sort_values('bill_length_mm')\n",
"display(df_sorted)\n",
"\n",
"# Resetting the index to the new order after sorting\n",
"df_sorted_reset = df_sorted.reset_index(drop=True)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame with reset index:\")\n",
"display(df_sorted_reset)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"Reset Index Function Documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/docs/reference/api/pandas.DataFrame.reset_index.html"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Inplace vs. Not Inplace\n",
"\n",
"tester = df_sorted.copy()\n",
"# Resetting the index to the new order after sorting not inplace\n",
"print(\"DataFrame with reset index not inplace:\")\n",
"display(tester.reset_index(drop=True))\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nOriginal Dataframe:\")\n",
"display(tester)\n",
"\n",
"# Resetting the index to the new order after sorting inplace\n",
"print(\"DataFrame with reset index inplace:\")\n",
"tester.reset_index(drop=True,inplace=True)\n",
"display(tester)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"#Another common example dataset\n",
"iris = sns.load_dataset(\"iris\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"
"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Introduction"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"Pandas is a library for working with tabular data. It was orignally based on the R data.frame library. \n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Loading and Displaying the Dataset\n",
"import pandas as pd\n",
"import seaborn as sns\n",
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
"import numpy as np\n",
"\n",
"from palmerpenguins import load_penguins\n",
"df = load_penguins()\n",
"\n",
"print(\"Type of the dataset:\", type(df))\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame using head command:\")\n",
"display(df.head())\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame using tail command:\")\n",
"display(df.tail())"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Key Concepts:\n",
"\n",
"- A DataFrame is a 2-dimensional data structure in pandas. It's like a spreadsheet or a table with rows and columns.\n",
"- Generally, \n",
" - Columns represent features (variables we measure or observe)\n",
" - Rows represent individual observations (in this case, each penguin)\n",
"\n",
"- In this dataset:\n",
" - Each row represents a single penguin\n",
" - Each column represents a feature (e.g., species, island, bill length)\n",
"\n",
"- Common functions for initial data exploration:\n",
" - df.head() Shows the first 5 rows by default\n",
" - df.info() Provides a concise summary of the DataFrame\n",
" - df.describe() Generates descriptive statistics for numerical columns"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Whole DataFrame Exploration\n",
"print(\"Summary statistics:\")\n",
"display(df.describe())\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nData types of columns:\")\n",
"display(df.dtypes)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nColumn names:\")\n",
"print(df.columns)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame info:\")\n",
"df.info()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Column Specific Operations\n",
"\n",
"# Using value counts to get the number of penguins for each species\n",
"species_counts = df['species'].value_counts()\n",
"print(\"Penguins per species:\")\n",
"print(species_counts)\n",
"\n",
"# Get the mean bill length\n",
"bill_length = df['bill_length_mm'].mean() # Can get the mode and sum\n",
"print(f'\\nAverage bill length: {bill_length}')\n",
"\n",
"# Get the mean bill length per species\n",
"species_bill_length = df.groupby('species')['bill_length_mm'].mean()\n",
"print(\"\\nAverage bill length per species:\")\n",
"print(species_bill_length)\n",
"\n",
"# Get the unique species\n",
"unique_species = df['species'].unique()\n",
"print(f\"\\nUnique species: {unique_species}\")\n",
"\n",
"# Get number of null values\n",
"boolean_vec = df.isnull()\n",
"print(f\"\\nBoolean_vec: {boolean_vec}\")\n",
"sum = boolean_vec.sum()\n",
"print(f\"\\nBoolean_vec sum: {sum}\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Data Cleaning\n",
"\n",
"# Examine original dataframe\n",
"print(\"Orifinal dataframe:\")\n",
"display(df)\n",
"\n",
"# Drop all rows with a null value\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe with non-null rows:\")\n",
"display(df.dropna())\n",
"\n",
"# Drop all columns with a null value\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe with non-null columns:\")\n",
"display(df.dropna(axis=1))\n",
"\n",
"# Replace all null values\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe with nulls replaced:\")\n",
"display(df.fillna(1))\n",
"\n",
"# Sort df based on column of interest\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe sorted based on column:\")\n",
"df_sorted = df.sort_values('bill_length_mm')\n",
"display(df_sorted)\n",
"\n",
"# Resetting the index to the new order after sorting\n",
"df_sorted_reset = df_sorted.reset_index(drop=True)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame with reset index:\")\n",
"display(df_sorted_reset)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"Reset Index Function Documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/docs/reference/api/pandas.DataFrame.reset_index.html"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Inplace vs. Not Inplace\n",
"\n",
"tester = df_sorted.copy()\n",
"# Resetting the index to the new order after sorting not inplace\n",
"print(\"DataFrame with reset index not inplace:\")\n",
"display(tester.reset_index(drop=True))\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nOriginal Dataframe:\")\n",
"display(tester)\n",
"\n",
"# Resetting the index to the new order after sorting inplace\n",
"print(\"DataFrame with reset index inplace:\")\n",
"tester.reset_index(drop=True,inplace=True)\n",
"display(tester)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"#Another common example dataset\n",
"iris = sns.load_dataset(\"iris\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
" "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercises 1\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Display the first and then the last 15 rows in a dataframe \n",
"\n",
"# 2. Use any function to explore the new dataset\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Display only the sepal_length column in the format of a pandas dataframe\n",
"\n",
"# 4. Display only sepal_length column in the format of a pandas series and check the type\n",
"\n",
"# 5. Get the names of all the species and check the type\n",
"\n",
"# 6. Get the total number of null values in the entire dataFrame\n",
"\n",
"# 7. Replace all null values w/ the mean value of that column (note: operation only works w/ numeric columns)\n",
"\n",
"# 8. Sort the dataframe in decending order based on a petal_length and reset the index without writing over the original dataframe\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Several different ways to subset/query a dataframe"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### By Column"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Selecting Data from DataFrame\n",
"\n",
"# Understanding Pandas Series\n",
"# 1. A Series is like a single column of data\n",
"# 2. It has an index (labels for each item) but no column names\n",
"# 3. A Series can have a name, which labels the whole Series\n",
"\n",
"print(\"Single column (as Series):\")\n",
"series = df['bill_length_mm']\n",
"display(series)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nSeries index (labels for each item):\")\n",
"print(series.index)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nSeries name:\")\n",
"print(series.name)\n",
"\n",
"# We can change the Series name\n",
"series.name = \"Bill Length\"\n",
"print(\"\\nUpdated Series name:\")\n",
"print(series.name)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Selecting Data from DataFrame Pt. 2\n",
"\n",
"# When we use double brackets, we get a DataFrame instead\n",
"print(\"Single column (as DataFrame):\")\n",
"single_column_df = df[['bill_length_mm']]\n",
"display(single_column_df)\n",
"print(\"Type:\", type(single_column_df))\n",
"\n",
"# Note: A Series is like a single labeled column, while a DataFrame \n",
"# is like a table with potentially many columns. The Series index is \n",
"# like row labels, and its name can become a column name in a DataFrame."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Key Concept: Series vs DataFrame in Column Selection\n",
"* Using double brackets [[]] selects columns and returns a DataFrame\n",
"* Using single brackets [] for a single column returns a Series\n",
"* A DataFrame is a 2D structure with both row and column labels\n",
"* A Series is a 1D structure with only row labels (index)\n",
"\n",
"* Note: Some operations work on Series, others on DataFrames, so it's helpful to know which one you're using."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### How can we visulize the distribution of this single variable better?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Basic Data Visualization\n",
"plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))\n",
"sns.histplot(df['bill_length_mm'], kde=True, bins=20)\n",
"plt.title('Distribution of Bill Length')\n",
"plt.xlabel('Bill Length (mm)')\n",
"plt.ylabel('Count')\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Helpful resources for data visulization in python: \n",
"- https://python-graph-gallery.com\n",
"- https://github.com/cxli233/FriendsDontLetFriends"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### By Row"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Data Selection\n",
"# Select specific rows and columns using iloc (integer-location based indexing)\n",
"print(\"Using iloc:\")\n",
"print(df.iloc[2, 2]) # Value at 3rd row, 3rd column\n",
"\n",
"# Select rows using loc (label-based indexing)\n",
"print(\"\\nUsing loc:\")\n",
"display(df.loc[3]) # 4th row\n",
"display(df.loc[0:3]) # First 4 rows\n",
"\n",
"# Query the DataFrame by condition\n",
"print(\"\\nUsing query:\")\n",
"display(df.query(\"year > 2008\"))\n",
"\n",
"# Query dataframe based on two conditions\n",
"\n",
"# Method 1\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 1 Dataframe:\")\n",
"yr_vec = df['year'] > 2008\n",
"island_vec = df['island'] == 'Biscoe'\n",
"\n",
"combine_vec = np.logical_and(yr_vec,island_vec)\n",
"display(df[combine_vec])\n",
"\n",
"#Method 2\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 2 Dataframe:\")\n",
"display(df[(yr_vec) & (island_vec)])"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercises 2\n",
"\n",
"display(iris.head())\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Get out the sepal_length column as a pandas series and rename the series\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Get the 5th row, 2nd column element using the iloc function\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Get the last 5 rows using the loc function and then iloc\n",
"\n",
"# 4. Visualize the distribution of the sepal length of the iris dataset\n",
"\n",
"# 5. Display only the rows that have a petal length greater than or equal to 1.5 and petal width greater than or equal to 0.5\n",
"\n",
"# 6. Display only the rows that meet either of two conditions\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Histograms allowed us to visualize the distribution of a singel feature, what about the relation between features? How do we decide our filtering condition with multiple features?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Create jointplots to determine relationships between specific variables\n",
"sns.jointplot(data=df, x=\"bill_length_mm\", y=\"bill_depth_mm\")\n",
"plt.show()\n",
"\n",
"sns.jointplot(data=df, x=\"body_mass_g\", y=\"flipper_length_mm\")\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Create pairplots to determine relationships between all numeric variables\n",
"sns.pairplot(df)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Different ways of visualizing the same data can lead to different interpretations\n",
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
"fig , ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(15,12), ncols=2,nrows=2)\n",
"sns.swarmplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[0,0],hue='species')\n",
"sns.violinplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[0,1])\n",
"sns.boxplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[1,0])\n",
"sns.barplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[1,1])\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercise 3\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Plot relation petal length and petal width\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Plot relationship between all numeric values\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Use two different plots to visualize the data for petal length for only the setosa and virginica species"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### After editing our dataframes how can we save them in a way that allows us to read them back in without having to redo our analysis?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Saving Pandas Dataframes\n",
"\n",
"df.to_csv('penguins.csv', index=False)\n",
"\n",
"df.to_excel('penguins.xlsx', index=False, sheet_name='Sheet1')"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Reading Pandas Dataframes\n",
"\n",
"df_csv = pd.read_csv('penguins.csv')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from CSV:\")\n",
"display(df_csv)\n",
"\n",
"df_excel = pd.read_excel('penguins.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet1')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from Excel:\")\n",
"display(df_excel)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercise 4\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Write the iris dataset to a csv\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Write the iris dataset to a excel\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Read in the iris dataset from the csv\n",
"\n",
"# 4. Read in the iris dataset from the excel\n",
"\n",
"# 5. Write to a file w semicolon as a seperator\n",
"\n",
"# 6. Read in the semicolon file\n"
]
}
],
"metadata": {
"kernelspec": {
"display_name": "Python 3 (ipykernel)",
"language": "python",
"name": "python3"
},
"language_info": {
"codemirror_mode": {
"name": "ipython",
"version": 3
},
"file_extension": ".py",
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
"name": "python",
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
"version": "3.9.-1"
}
},
"nbformat": 4,
"nbformat_minor": 4
}
"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercises 1\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Display the first and then the last 15 rows in a dataframe \n",
"\n",
"# 2. Use any function to explore the new dataset\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Display only the sepal_length column in the format of a pandas dataframe\n",
"\n",
"# 4. Display only sepal_length column in the format of a pandas series and check the type\n",
"\n",
"# 5. Get the names of all the species and check the type\n",
"\n",
"# 6. Get the total number of null values in the entire dataFrame\n",
"\n",
"# 7. Replace all null values w/ the mean value of that column (note: operation only works w/ numeric columns)\n",
"\n",
"# 8. Sort the dataframe in decending order based on a petal_length and reset the index without writing over the original dataframe\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Several different ways to subset/query a dataframe"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### By Column"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Selecting Data from DataFrame\n",
"\n",
"# Understanding Pandas Series\n",
"# 1. A Series is like a single column of data\n",
"# 2. It has an index (labels for each item) but no column names\n",
"# 3. A Series can have a name, which labels the whole Series\n",
"\n",
"print(\"Single column (as Series):\")\n",
"series = df['bill_length_mm']\n",
"display(series)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nSeries index (labels for each item):\")\n",
"print(series.index)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nSeries name:\")\n",
"print(series.name)\n",
"\n",
"# We can change the Series name\n",
"series.name = \"Bill Length\"\n",
"print(\"\\nUpdated Series name:\")\n",
"print(series.name)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Selecting Data from DataFrame Pt. 2\n",
"\n",
"# When we use double brackets, we get a DataFrame instead\n",
"print(\"Single column (as DataFrame):\")\n",
"single_column_df = df[['bill_length_mm']]\n",
"display(single_column_df)\n",
"print(\"Type:\", type(single_column_df))\n",
"\n",
"# Note: A Series is like a single labeled column, while a DataFrame \n",
"# is like a table with potentially many columns. The Series index is \n",
"# like row labels, and its name can become a column name in a DataFrame."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Key Concept: Series vs DataFrame in Column Selection\n",
"* Using double brackets [[]] selects columns and returns a DataFrame\n",
"* Using single brackets [] for a single column returns a Series\n",
"* A DataFrame is a 2D structure with both row and column labels\n",
"* A Series is a 1D structure with only row labels (index)\n",
"\n",
"* Note: Some operations work on Series, others on DataFrames, so it's helpful to know which one you're using."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### How can we visulize the distribution of this single variable better?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Basic Data Visualization\n",
"plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))\n",
"sns.histplot(df['bill_length_mm'], kde=True, bins=20)\n",
"plt.title('Distribution of Bill Length')\n",
"plt.xlabel('Bill Length (mm)')\n",
"plt.ylabel('Count')\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Helpful resources for data visulization in python: \n",
"- https://python-graph-gallery.com\n",
"- https://github.com/cxli233/FriendsDontLetFriends"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### By Row"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Data Selection\n",
"# Select specific rows and columns using iloc (integer-location based indexing)\n",
"print(\"Using iloc:\")\n",
"print(df.iloc[2, 2]) # Value at 3rd row, 3rd column\n",
"\n",
"# Select rows using loc (label-based indexing)\n",
"print(\"\\nUsing loc:\")\n",
"display(df.loc[3]) # 4th row\n",
"display(df.loc[0:3]) # First 4 rows\n",
"\n",
"# Query the DataFrame by condition\n",
"print(\"\\nUsing query:\")\n",
"display(df.query(\"year > 2008\"))\n",
"\n",
"# Query dataframe based on two conditions\n",
"\n",
"# Method 1\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 1 Dataframe:\")\n",
"yr_vec = df['year'] > 2008\n",
"island_vec = df['island'] == 'Biscoe'\n",
"\n",
"combine_vec = np.logical_and(yr_vec,island_vec)\n",
"display(df[combine_vec])\n",
"\n",
"#Method 2\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 2 Dataframe:\")\n",
"display(df[(yr_vec) & (island_vec)])"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercises 2\n",
"\n",
"display(iris.head())\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Get out the sepal_length column as a pandas series and rename the series\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Get the 5th row, 2nd column element using the iloc function\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Get the last 5 rows using the loc function and then iloc\n",
"\n",
"# 4. Visualize the distribution of the sepal length of the iris dataset\n",
"\n",
"# 5. Display only the rows that have a petal length greater than or equal to 1.5 and petal width greater than or equal to 0.5\n",
"\n",
"# 6. Display only the rows that meet either of two conditions\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Histograms allowed us to visualize the distribution of a singel feature, what about the relation between features? How do we decide our filtering condition with multiple features?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Create jointplots to determine relationships between specific variables\n",
"sns.jointplot(data=df, x=\"bill_length_mm\", y=\"bill_depth_mm\")\n",
"plt.show()\n",
"\n",
"sns.jointplot(data=df, x=\"body_mass_g\", y=\"flipper_length_mm\")\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Create pairplots to determine relationships between all numeric variables\n",
"sns.pairplot(df)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Different ways of visualizing the same data can lead to different interpretations\n",
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
"fig , ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(15,12), ncols=2,nrows=2)\n",
"sns.swarmplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[0,0],hue='species')\n",
"sns.violinplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[0,1])\n",
"sns.boxplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[1,0])\n",
"sns.barplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[1,1])\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercise 3\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Plot relation petal length and petal width\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Plot relationship between all numeric values\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Use two different plots to visualize the data for petal length for only the setosa and virginica species"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### After editing our dataframes how can we save them in a way that allows us to read them back in without having to redo our analysis?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Saving Pandas Dataframes\n",
"\n",
"df.to_csv('penguins.csv', index=False)\n",
"\n",
"df.to_excel('penguins.xlsx', index=False, sheet_name='Sheet1')"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Reading Pandas Dataframes\n",
"\n",
"df_csv = pd.read_csv('penguins.csv')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from CSV:\")\n",
"display(df_csv)\n",
"\n",
"df_excel = pd.read_excel('penguins.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet1')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from Excel:\")\n",
"display(df_excel)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercise 4\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Write the iris dataset to a csv\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Write the iris dataset to a excel\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Read in the iris dataset from the csv\n",
"\n",
"# 4. Read in the iris dataset from the excel\n",
"\n",
"# 5. Write to a file w semicolon as a seperator\n",
"\n",
"# 6. Read in the semicolon file\n"
]
}
],
"metadata": {
"kernelspec": {
"display_name": "Python 3 (ipykernel)",
"language": "python",
"name": "python3"
},
"language_info": {
"codemirror_mode": {
"name": "ipython",
"version": 3
},
"file_extension": ".py",
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
"name": "python",
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
"version": "3.9.-1"
}
},
"nbformat": 4,
"nbformat_minor": 4
}
 \n",
"
\n",
" "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Introduction"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"Pandas is a library for working with tabular data. It was orignally based on the R data.frame library. \n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Loading and Displaying the Dataset\n",
"import pandas as pd\n",
"import seaborn as sns\n",
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
"import numpy as np\n",
"\n",
"from palmerpenguins import load_penguins\n",
"df = load_penguins()\n",
"\n",
"print(\"Type of the dataset:\", type(df))\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame using head command:\")\n",
"display(df.head())\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame using tail command:\")\n",
"display(df.tail())"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Key Concepts:\n",
"\n",
"- A DataFrame is a 2-dimensional data structure in pandas. It's like a spreadsheet or a table with rows and columns.\n",
"- Generally, \n",
" - Columns represent features (variables we measure or observe)\n",
" - Rows represent individual observations (in this case, each penguin)\n",
"\n",
"- In this dataset:\n",
" - Each row represents a single penguin\n",
" - Each column represents a feature (e.g., species, island, bill length)\n",
"\n",
"- Common functions for initial data exploration:\n",
" - df.head() Shows the first 5 rows by default\n",
" - df.info() Provides a concise summary of the DataFrame\n",
" - df.describe() Generates descriptive statistics for numerical columns"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Whole DataFrame Exploration\n",
"print(\"Summary statistics:\")\n",
"display(df.describe())\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nData types of columns:\")\n",
"display(df.dtypes)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nColumn names:\")\n",
"print(df.columns)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame info:\")\n",
"df.info()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Column Specific Operations\n",
"\n",
"# Using value counts to get the number of penguins for each species\n",
"species_counts = df['species'].value_counts()\n",
"print(\"Penguins per species:\")\n",
"print(species_counts)\n",
"\n",
"# Get the mean bill length\n",
"bill_length = df['bill_length_mm'].mean() # Can get the mode and sum\n",
"print(f'\\nAverage bill length: {bill_length}')\n",
"\n",
"# Get the mean bill length per species\n",
"species_bill_length = df.groupby('species')['bill_length_mm'].mean()\n",
"print(\"\\nAverage bill length per species:\")\n",
"print(species_bill_length)\n",
"\n",
"# Get the unique species\n",
"unique_species = df['species'].unique()\n",
"print(f\"\\nUnique species: {unique_species}\")\n",
"\n",
"# Get number of null values\n",
"boolean_vec = df.isnull()\n",
"print(f\"\\nBoolean_vec: {boolean_vec}\")\n",
"sum = boolean_vec.sum()\n",
"print(f\"\\nBoolean_vec sum: {sum}\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Data Cleaning\n",
"\n",
"# Examine original dataframe\n",
"print(\"Orifinal dataframe:\")\n",
"display(df)\n",
"\n",
"# Drop all rows with a null value\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe with non-null rows:\")\n",
"display(df.dropna())\n",
"\n",
"# Drop all columns with a null value\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe with non-null columns:\")\n",
"display(df.dropna(axis=1))\n",
"\n",
"# Replace all null values\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe with nulls replaced:\")\n",
"display(df.fillna(1))\n",
"\n",
"# Sort df based on column of interest\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe sorted based on column:\")\n",
"df_sorted = df.sort_values('bill_length_mm')\n",
"display(df_sorted)\n",
"\n",
"# Resetting the index to the new order after sorting\n",
"df_sorted_reset = df_sorted.reset_index(drop=True)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame with reset index:\")\n",
"display(df_sorted_reset)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"Reset Index Function Documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/docs/reference/api/pandas.DataFrame.reset_index.html"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Inplace vs. Not Inplace\n",
"\n",
"tester = df_sorted.copy()\n",
"# Resetting the index to the new order after sorting not inplace\n",
"print(\"DataFrame with reset index not inplace:\")\n",
"display(tester.reset_index(drop=True))\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nOriginal Dataframe:\")\n",
"display(tester)\n",
"\n",
"# Resetting the index to the new order after sorting inplace\n",
"print(\"DataFrame with reset index inplace:\")\n",
"tester.reset_index(drop=True,inplace=True)\n",
"display(tester)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"#Another common example dataset\n",
"iris = sns.load_dataset(\"iris\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"
"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Introduction"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"Pandas is a library for working with tabular data. It was orignally based on the R data.frame library. \n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Loading and Displaying the Dataset\n",
"import pandas as pd\n",
"import seaborn as sns\n",
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
"import numpy as np\n",
"\n",
"from palmerpenguins import load_penguins\n",
"df = load_penguins()\n",
"\n",
"print(\"Type of the dataset:\", type(df))\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame using head command:\")\n",
"display(df.head())\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame using tail command:\")\n",
"display(df.tail())"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Key Concepts:\n",
"\n",
"- A DataFrame is a 2-dimensional data structure in pandas. It's like a spreadsheet or a table with rows and columns.\n",
"- Generally, \n",
" - Columns represent features (variables we measure or observe)\n",
" - Rows represent individual observations (in this case, each penguin)\n",
"\n",
"- In this dataset:\n",
" - Each row represents a single penguin\n",
" - Each column represents a feature (e.g., species, island, bill length)\n",
"\n",
"- Common functions for initial data exploration:\n",
" - df.head() Shows the first 5 rows by default\n",
" - df.info() Provides a concise summary of the DataFrame\n",
" - df.describe() Generates descriptive statistics for numerical columns"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Whole DataFrame Exploration\n",
"print(\"Summary statistics:\")\n",
"display(df.describe())\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nData types of columns:\")\n",
"display(df.dtypes)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nColumn names:\")\n",
"print(df.columns)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame info:\")\n",
"df.info()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Column Specific Operations\n",
"\n",
"# Using value counts to get the number of penguins for each species\n",
"species_counts = df['species'].value_counts()\n",
"print(\"Penguins per species:\")\n",
"print(species_counts)\n",
"\n",
"# Get the mean bill length\n",
"bill_length = df['bill_length_mm'].mean() # Can get the mode and sum\n",
"print(f'\\nAverage bill length: {bill_length}')\n",
"\n",
"# Get the mean bill length per species\n",
"species_bill_length = df.groupby('species')['bill_length_mm'].mean()\n",
"print(\"\\nAverage bill length per species:\")\n",
"print(species_bill_length)\n",
"\n",
"# Get the unique species\n",
"unique_species = df['species'].unique()\n",
"print(f\"\\nUnique species: {unique_species}\")\n",
"\n",
"# Get number of null values\n",
"boolean_vec = df.isnull()\n",
"print(f\"\\nBoolean_vec: {boolean_vec}\")\n",
"sum = boolean_vec.sum()\n",
"print(f\"\\nBoolean_vec sum: {sum}\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Data Cleaning\n",
"\n",
"# Examine original dataframe\n",
"print(\"Orifinal dataframe:\")\n",
"display(df)\n",
"\n",
"# Drop all rows with a null value\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe with non-null rows:\")\n",
"display(df.dropna())\n",
"\n",
"# Drop all columns with a null value\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe with non-null columns:\")\n",
"display(df.dropna(axis=1))\n",
"\n",
"# Replace all null values\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe with nulls replaced:\")\n",
"display(df.fillna(1))\n",
"\n",
"# Sort df based on column of interest\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe sorted based on column:\")\n",
"df_sorted = df.sort_values('bill_length_mm')\n",
"display(df_sorted)\n",
"\n",
"# Resetting the index to the new order after sorting\n",
"df_sorted_reset = df_sorted.reset_index(drop=True)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame with reset index:\")\n",
"display(df_sorted_reset)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"Reset Index Function Documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/docs/reference/api/pandas.DataFrame.reset_index.html"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Inplace vs. Not Inplace\n",
"\n",
"tester = df_sorted.copy()\n",
"# Resetting the index to the new order after sorting not inplace\n",
"print(\"DataFrame with reset index not inplace:\")\n",
"display(tester.reset_index(drop=True))\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nOriginal Dataframe:\")\n",
"display(tester)\n",
"\n",
"# Resetting the index to the new order after sorting inplace\n",
"print(\"DataFrame with reset index inplace:\")\n",
"tester.reset_index(drop=True,inplace=True)\n",
"display(tester)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"#Another common example dataset\n",
"iris = sns.load_dataset(\"iris\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
" "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercises 1\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Display the first and then the last 15 rows in a dataframe \n",
"\n",
"# 2. Use any function to explore the new dataset\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Display only the sepal_length column in the format of a pandas dataframe\n",
"\n",
"# 4. Display only sepal_length column in the format of a pandas series and check the type\n",
"\n",
"# 5. Get the names of all the species and check the type\n",
"\n",
"# 6. Get the total number of null values in the entire dataFrame\n",
"\n",
"# 7. Replace all null values w/ the mean value of that column (note: operation only works w/ numeric columns)\n",
"\n",
"# 8. Sort the dataframe in decending order based on a petal_length and reset the index without writing over the original dataframe\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Several different ways to subset/query a dataframe"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### By Column"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Selecting Data from DataFrame\n",
"\n",
"# Understanding Pandas Series\n",
"# 1. A Series is like a single column of data\n",
"# 2. It has an index (labels for each item) but no column names\n",
"# 3. A Series can have a name, which labels the whole Series\n",
"\n",
"print(\"Single column (as Series):\")\n",
"series = df['bill_length_mm']\n",
"display(series)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nSeries index (labels for each item):\")\n",
"print(series.index)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nSeries name:\")\n",
"print(series.name)\n",
"\n",
"# We can change the Series name\n",
"series.name = \"Bill Length\"\n",
"print(\"\\nUpdated Series name:\")\n",
"print(series.name)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Selecting Data from DataFrame Pt. 2\n",
"\n",
"# When we use double brackets, we get a DataFrame instead\n",
"print(\"Single column (as DataFrame):\")\n",
"single_column_df = df[['bill_length_mm']]\n",
"display(single_column_df)\n",
"print(\"Type:\", type(single_column_df))\n",
"\n",
"# Note: A Series is like a single labeled column, while a DataFrame \n",
"# is like a table with potentially many columns. The Series index is \n",
"# like row labels, and its name can become a column name in a DataFrame."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Key Concept: Series vs DataFrame in Column Selection\n",
"* Using double brackets [[]] selects columns and returns a DataFrame\n",
"* Using single brackets [] for a single column returns a Series\n",
"* A DataFrame is a 2D structure with both row and column labels\n",
"* A Series is a 1D structure with only row labels (index)\n",
"\n",
"* Note: Some operations work on Series, others on DataFrames, so it's helpful to know which one you're using."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### How can we visulize the distribution of this single variable better?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Basic Data Visualization\n",
"plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))\n",
"sns.histplot(df['bill_length_mm'], kde=True, bins=20)\n",
"plt.title('Distribution of Bill Length')\n",
"plt.xlabel('Bill Length (mm)')\n",
"plt.ylabel('Count')\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Helpful resources for data visulization in python: \n",
"- https://python-graph-gallery.com\n",
"- https://github.com/cxli233/FriendsDontLetFriends"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### By Row"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Data Selection\n",
"# Select specific rows and columns using iloc (integer-location based indexing)\n",
"print(\"Using iloc:\")\n",
"print(df.iloc[2, 2]) # Value at 3rd row, 3rd column\n",
"\n",
"# Select rows using loc (label-based indexing)\n",
"print(\"\\nUsing loc:\")\n",
"display(df.loc[3]) # 4th row\n",
"display(df.loc[0:3]) # First 4 rows\n",
"\n",
"# Query the DataFrame by condition\n",
"print(\"\\nUsing query:\")\n",
"display(df.query(\"year > 2008\"))\n",
"\n",
"# Query dataframe based on two conditions\n",
"\n",
"# Method 1\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 1 Dataframe:\")\n",
"yr_vec = df['year'] > 2008\n",
"island_vec = df['island'] == 'Biscoe'\n",
"\n",
"combine_vec = np.logical_and(yr_vec,island_vec)\n",
"display(df[combine_vec])\n",
"\n",
"#Method 2\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 2 Dataframe:\")\n",
"display(df[(yr_vec) & (island_vec)])"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercises 2\n",
"\n",
"display(iris.head())\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Get out the sepal_length column as a pandas series and rename the series\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Get the 5th row, 2nd column element using the iloc function\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Get the last 5 rows using the loc function and then iloc\n",
"\n",
"# 4. Visualize the distribution of the sepal length of the iris dataset\n",
"\n",
"# 5. Display only the rows that have a petal length greater than or equal to 1.5 and petal width greater than or equal to 0.5\n",
"\n",
"# 6. Display only the rows that meet either of two conditions\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Histograms allowed us to visualize the distribution of a singel feature, what about the relation between features? How do we decide our filtering condition with multiple features?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Create jointplots to determine relationships between specific variables\n",
"sns.jointplot(data=df, x=\"bill_length_mm\", y=\"bill_depth_mm\")\n",
"plt.show()\n",
"\n",
"sns.jointplot(data=df, x=\"body_mass_g\", y=\"flipper_length_mm\")\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Create pairplots to determine relationships between all numeric variables\n",
"sns.pairplot(df)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Different ways of visualizing the same data can lead to different interpretations\n",
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
"fig , ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(15,12), ncols=2,nrows=2)\n",
"sns.swarmplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[0,0],hue='species')\n",
"sns.violinplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[0,1])\n",
"sns.boxplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[1,0])\n",
"sns.barplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[1,1])\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercise 3\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Plot relation petal length and petal width\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Plot relationship between all numeric values\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Use two different plots to visualize the data for petal length for only the setosa and virginica species"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### After editing our dataframes how can we save them in a way that allows us to read them back in without having to redo our analysis?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Saving Pandas Dataframes\n",
"\n",
"df.to_csv('penguins.csv', index=False)\n",
"\n",
"df.to_excel('penguins.xlsx', index=False, sheet_name='Sheet1')"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Reading Pandas Dataframes\n",
"\n",
"df_csv = pd.read_csv('penguins.csv')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from CSV:\")\n",
"display(df_csv)\n",
"\n",
"df_excel = pd.read_excel('penguins.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet1')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from Excel:\")\n",
"display(df_excel)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercise 4\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Write the iris dataset to a csv\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Write the iris dataset to a excel\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Read in the iris dataset from the csv\n",
"\n",
"# 4. Read in the iris dataset from the excel\n",
"\n",
"# 5. Write to a file w semicolon as a seperator\n",
"\n",
"# 6. Read in the semicolon file\n"
]
}
],
"metadata": {
"kernelspec": {
"display_name": "Python 3 (ipykernel)",
"language": "python",
"name": "python3"
},
"language_info": {
"codemirror_mode": {
"name": "ipython",
"version": 3
},
"file_extension": ".py",
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
"name": "python",
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
"version": "3.9.-1"
}
},
"nbformat": 4,
"nbformat_minor": 4
}
"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercises 1\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Display the first and then the last 15 rows in a dataframe \n",
"\n",
"# 2. Use any function to explore the new dataset\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Display only the sepal_length column in the format of a pandas dataframe\n",
"\n",
"# 4. Display only sepal_length column in the format of a pandas series and check the type\n",
"\n",
"# 5. Get the names of all the species and check the type\n",
"\n",
"# 6. Get the total number of null values in the entire dataFrame\n",
"\n",
"# 7. Replace all null values w/ the mean value of that column (note: operation only works w/ numeric columns)\n",
"\n",
"# 8. Sort the dataframe in decending order based on a petal_length and reset the index without writing over the original dataframe\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Several different ways to subset/query a dataframe"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### By Column"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Selecting Data from DataFrame\n",
"\n",
"# Understanding Pandas Series\n",
"# 1. A Series is like a single column of data\n",
"# 2. It has an index (labels for each item) but no column names\n",
"# 3. A Series can have a name, which labels the whole Series\n",
"\n",
"print(\"Single column (as Series):\")\n",
"series = df['bill_length_mm']\n",
"display(series)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nSeries index (labels for each item):\")\n",
"print(series.index)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nSeries name:\")\n",
"print(series.name)\n",
"\n",
"# We can change the Series name\n",
"series.name = \"Bill Length\"\n",
"print(\"\\nUpdated Series name:\")\n",
"print(series.name)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Selecting Data from DataFrame Pt. 2\n",
"\n",
"# When we use double brackets, we get a DataFrame instead\n",
"print(\"Single column (as DataFrame):\")\n",
"single_column_df = df[['bill_length_mm']]\n",
"display(single_column_df)\n",
"print(\"Type:\", type(single_column_df))\n",
"\n",
"# Note: A Series is like a single labeled column, while a DataFrame \n",
"# is like a table with potentially many columns. The Series index is \n",
"# like row labels, and its name can become a column name in a DataFrame."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Key Concept: Series vs DataFrame in Column Selection\n",
"* Using double brackets [[]] selects columns and returns a DataFrame\n",
"* Using single brackets [] for a single column returns a Series\n",
"* A DataFrame is a 2D structure with both row and column labels\n",
"* A Series is a 1D structure with only row labels (index)\n",
"\n",
"* Note: Some operations work on Series, others on DataFrames, so it's helpful to know which one you're using."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### How can we visulize the distribution of this single variable better?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Basic Data Visualization\n",
"plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))\n",
"sns.histplot(df['bill_length_mm'], kde=True, bins=20)\n",
"plt.title('Distribution of Bill Length')\n",
"plt.xlabel('Bill Length (mm)')\n",
"plt.ylabel('Count')\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Helpful resources for data visulization in python: \n",
"- https://python-graph-gallery.com\n",
"- https://github.com/cxli233/FriendsDontLetFriends"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### By Row"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Data Selection\n",
"# Select specific rows and columns using iloc (integer-location based indexing)\n",
"print(\"Using iloc:\")\n",
"print(df.iloc[2, 2]) # Value at 3rd row, 3rd column\n",
"\n",
"# Select rows using loc (label-based indexing)\n",
"print(\"\\nUsing loc:\")\n",
"display(df.loc[3]) # 4th row\n",
"display(df.loc[0:3]) # First 4 rows\n",
"\n",
"# Query the DataFrame by condition\n",
"print(\"\\nUsing query:\")\n",
"display(df.query(\"year > 2008\"))\n",
"\n",
"# Query dataframe based on two conditions\n",
"\n",
"# Method 1\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 1 Dataframe:\")\n",
"yr_vec = df['year'] > 2008\n",
"island_vec = df['island'] == 'Biscoe'\n",
"\n",
"combine_vec = np.logical_and(yr_vec,island_vec)\n",
"display(df[combine_vec])\n",
"\n",
"#Method 2\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 2 Dataframe:\")\n",
"display(df[(yr_vec) & (island_vec)])"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercises 2\n",
"\n",
"display(iris.head())\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Get out the sepal_length column as a pandas series and rename the series\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Get the 5th row, 2nd column element using the iloc function\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Get the last 5 rows using the loc function and then iloc\n",
"\n",
"# 4. Visualize the distribution of the sepal length of the iris dataset\n",
"\n",
"# 5. Display only the rows that have a petal length greater than or equal to 1.5 and petal width greater than or equal to 0.5\n",
"\n",
"# 6. Display only the rows that meet either of two conditions\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Histograms allowed us to visualize the distribution of a singel feature, what about the relation between features? How do we decide our filtering condition with multiple features?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Create jointplots to determine relationships between specific variables\n",
"sns.jointplot(data=df, x=\"bill_length_mm\", y=\"bill_depth_mm\")\n",
"plt.show()\n",
"\n",
"sns.jointplot(data=df, x=\"body_mass_g\", y=\"flipper_length_mm\")\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Create pairplots to determine relationships between all numeric variables\n",
"sns.pairplot(df)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Different ways of visualizing the same data can lead to different interpretations\n",
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
"fig , ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(15,12), ncols=2,nrows=2)\n",
"sns.swarmplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[0,0],hue='species')\n",
"sns.violinplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[0,1])\n",
"sns.boxplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[1,0])\n",
"sns.barplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[1,1])\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercise 3\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Plot relation petal length and petal width\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Plot relationship between all numeric values\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Use two different plots to visualize the data for petal length for only the setosa and virginica species"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### After editing our dataframes how can we save them in a way that allows us to read them back in without having to redo our analysis?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Saving Pandas Dataframes\n",
"\n",
"df.to_csv('penguins.csv', index=False)\n",
"\n",
"df.to_excel('penguins.xlsx', index=False, sheet_name='Sheet1')"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Reading Pandas Dataframes\n",
"\n",
"df_csv = pd.read_csv('penguins.csv')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from CSV:\")\n",
"display(df_csv)\n",
"\n",
"df_excel = pd.read_excel('penguins.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet1')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from Excel:\")\n",
"display(df_excel)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercise 4\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Write the iris dataset to a csv\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Write the iris dataset to a excel\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Read in the iris dataset from the csv\n",
"\n",
"# 4. Read in the iris dataset from the excel\n",
"\n",
"# 5. Write to a file w semicolon as a seperator\n",
"\n",
"# 6. Read in the semicolon file\n"
]
}
],
"metadata": {
"kernelspec": {
"display_name": "Python 3 (ipykernel)",
"language": "python",
"name": "python3"
},
"language_info": {
"codemirror_mode": {
"name": "ipython",
"version": 3
},
"file_extension": ".py",
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
"name": "python",
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
"version": "3.9.-1"
}
},
"nbformat": 4,
"nbformat_minor": 4
}