{
"cells": [
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"# Notebook 4: Pandas and visulization I."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"Here we will start using Pandas. Pandas is the standard way of working with tabular data. A great resource to learn more about Pandas is: http://pandas.pydata.org/"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Installation and downloads"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# downloading the example dataset that we'll use for this class. \n",
"# Pandas is already installed in colab by default as its very frequently used.\n",
"!pip -q install palmerpenguins"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
" \n",
"
\n",
" "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Introduction"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"Pandas is a library for working with tabular data. It was orignally based on the R data.frame library. \n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Loading and Displaying the Dataset\n",
"import pandas as pd\n",
"import seaborn as sns\n",
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
"import numpy as np\n",
"\n",
"from palmerpenguins import load_penguins\n",
"df = load_penguins()\n",
"\n",
"print(\"Type of the dataset:\", type(df))\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame using head command:\")\n",
"display(df.head())\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame using tail command:\")\n",
"display(df.tail())"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Key Concepts:\n",
"\n",
"- A DataFrame is a 2-dimensional data structure in pandas. It's like a spreadsheet or a table with rows and columns.\n",
"- Generally, \n",
" - Columns represent features (variables we measure or observe)\n",
" - Rows represent individual observations (in this case, each penguin)\n",
"\n",
"- In this dataset:\n",
" - Each row represents a single penguin\n",
" - Each column represents a feature (e.g., species, island, bill length)\n",
"\n",
"- Common functions for initial data exploration:\n",
" - df.head() Shows the first 5 rows by default\n",
" - df.info() Provides a concise summary of the DataFrame\n",
" - df.describe() Generates descriptive statistics for numerical columns"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Whole DataFrame Exploration\n",
"print(\"Summary statistics:\")\n",
"display(df.describe())\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nData types of columns:\")\n",
"display(df.dtypes)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nColumn names:\")\n",
"print(df.columns)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame info:\")\n",
"df.info()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Column Specific Operations\n",
"\n",
"# Using value counts to get the number of penguins for each species\n",
"species_counts = df['species'].value_counts()\n",
"print(\"Penguins per species:\")\n",
"print(species_counts)\n",
"\n",
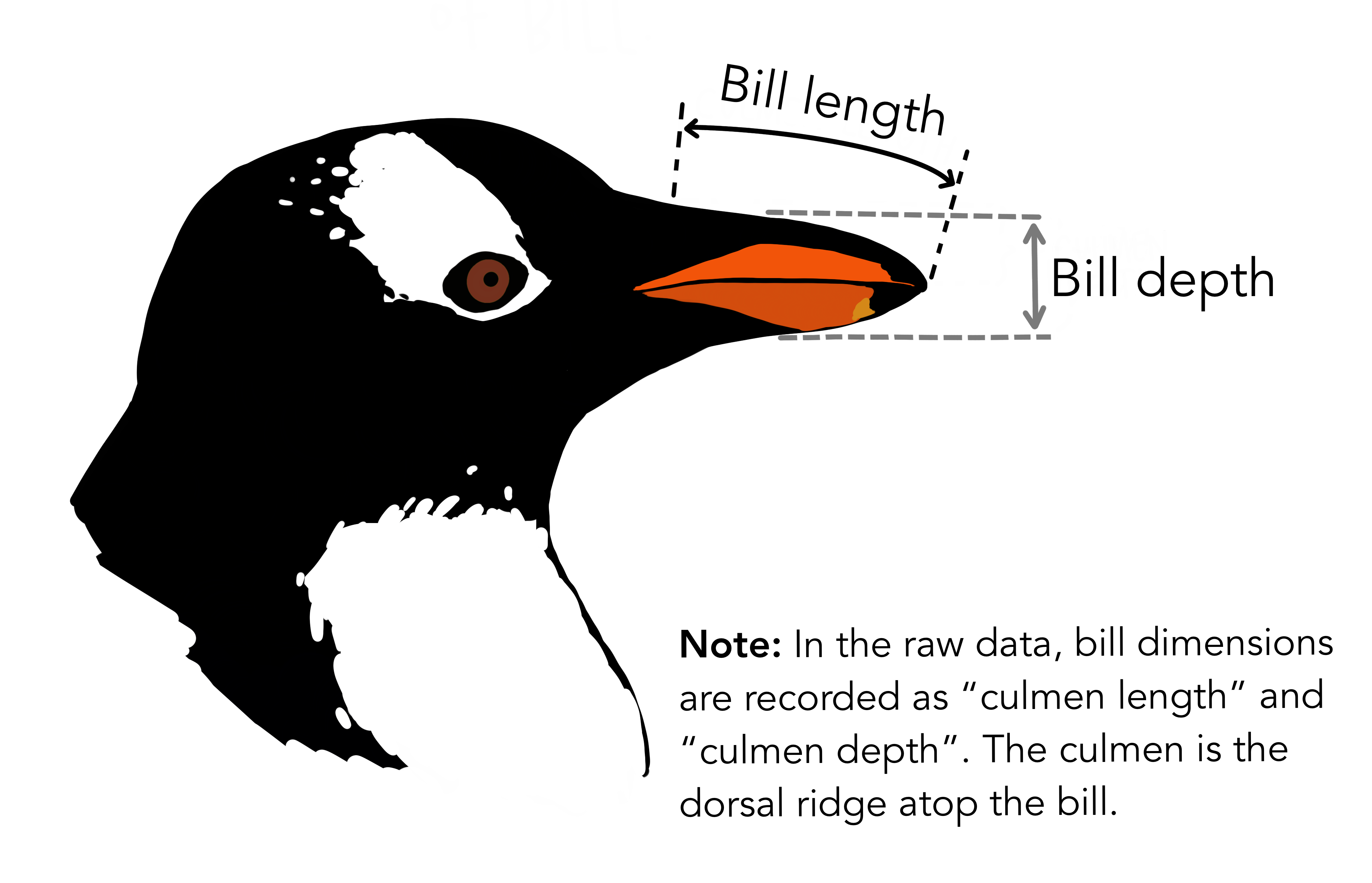
"# Get the mean bill length\n",
"bill_length = df['bill_length_mm'].mean() # Can get the mode and sum\n",
"print(f'\\nAverage bill length: {bill_length}')\n",
"\n",
"# Get the mean bill length per species\n",
"species_bill_length = df.groupby('species')['bill_length_mm'].mean()\n",
"print(\"\\nAverage bill length per species:\")\n",
"print(species_bill_length)\n",
"\n",
"# Get the unique species\n",
"unique_species = df['species'].unique()\n",
"print(f\"\\nUnique species: {unique_species}\")\n",
"\n",
"# Get number of null values\n",
"boolean_vec = df.isnull()\n",
"print(f\"\\nBoolean_vec: {boolean_vec}\")\n",
"sum = boolean_vec.sum()\n",
"print(f\"\\nBoolean_vec sum: {sum}\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Data Cleaning\n",
"\n",
"# Examine original dataframe\n",
"print(\"Orifinal dataframe:\")\n",
"display(df)\n",
"\n",
"# Drop all rows with a null value\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe with non-null rows:\")\n",
"display(df.dropna())\n",
"\n",
"# Drop all columns with a null value\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe with non-null columns:\")\n",
"display(df.dropna(axis=1))\n",
"\n",
"# Replace all null values\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe with nulls replaced:\")\n",
"display(df.fillna(1))\n",
"\n",
"# Sort df based on column of interest\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe sorted based on column:\")\n",
"df_sorted = df.sort_values('bill_length_mm')\n",
"display(df_sorted)\n",
"\n",
"# Resetting the index to the new order after sorting\n",
"df_sorted_reset = df_sorted.reset_index(drop=True)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame with reset index:\")\n",
"display(df_sorted_reset)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"Reset Index Function Documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/docs/reference/api/pandas.DataFrame.reset_index.html"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Inplace vs. Not Inplace\n",
"\n",
"tester = df_sorted.copy()\n",
"# Resetting the index to the new order after sorting not inplace\n",
"print(\"DataFrame with reset index not inplace:\")\n",
"display(tester.reset_index(drop=True))\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nOriginal Dataframe:\")\n",
"display(tester)\n",
"\n",
"# Resetting the index to the new order after sorting inplace\n",
"print(\"DataFrame with reset index inplace:\")\n",
"tester.reset_index(drop=True,inplace=True)\n",
"display(tester)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"#Another common example dataset\n",
"iris = sns.load_dataset(\"iris\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"
"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Introduction"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"Pandas is a library for working with tabular data. It was orignally based on the R data.frame library. \n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Loading and Displaying the Dataset\n",
"import pandas as pd\n",
"import seaborn as sns\n",
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
"import numpy as np\n",
"\n",
"from palmerpenguins import load_penguins\n",
"df = load_penguins()\n",
"\n",
"print(\"Type of the dataset:\", type(df))\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame using head command:\")\n",
"display(df.head())\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame using tail command:\")\n",
"display(df.tail())"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Key Concepts:\n",
"\n",
"- A DataFrame is a 2-dimensional data structure in pandas. It's like a spreadsheet or a table with rows and columns.\n",
"- Generally, \n",
" - Columns represent features (variables we measure or observe)\n",
" - Rows represent individual observations (in this case, each penguin)\n",
"\n",
"- In this dataset:\n",
" - Each row represents a single penguin\n",
" - Each column represents a feature (e.g., species, island, bill length)\n",
"\n",
"- Common functions for initial data exploration:\n",
" - df.head() Shows the first 5 rows by default\n",
" - df.info() Provides a concise summary of the DataFrame\n",
" - df.describe() Generates descriptive statistics for numerical columns"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Whole DataFrame Exploration\n",
"print(\"Summary statistics:\")\n",
"display(df.describe())\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nData types of columns:\")\n",
"display(df.dtypes)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nColumn names:\")\n",
"print(df.columns)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame info:\")\n",
"df.info()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Column Specific Operations\n",
"\n",
"# Using value counts to get the number of penguins for each species\n",
"species_counts = df['species'].value_counts()\n",
"print(\"Penguins per species:\")\n",
"print(species_counts)\n",
"\n",
"# Get the mean bill length\n",
"bill_length = df['bill_length_mm'].mean() # Can get the mode and sum\n",
"print(f'\\nAverage bill length: {bill_length}')\n",
"\n",
"# Get the mean bill length per species\n",
"species_bill_length = df.groupby('species')['bill_length_mm'].mean()\n",
"print(\"\\nAverage bill length per species:\")\n",
"print(species_bill_length)\n",
"\n",
"# Get the unique species\n",
"unique_species = df['species'].unique()\n",
"print(f\"\\nUnique species: {unique_species}\")\n",
"\n",
"# Get number of null values\n",
"boolean_vec = df.isnull()\n",
"print(f\"\\nBoolean_vec: {boolean_vec}\")\n",
"sum = boolean_vec.sum()\n",
"print(f\"\\nBoolean_vec sum: {sum}\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Data Cleaning\n",
"\n",
"# Examine original dataframe\n",
"print(\"Orifinal dataframe:\")\n",
"display(df)\n",
"\n",
"# Drop all rows with a null value\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe with non-null rows:\")\n",
"display(df.dropna())\n",
"\n",
"# Drop all columns with a null value\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe with non-null columns:\")\n",
"display(df.dropna(axis=1))\n",
"\n",
"# Replace all null values\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe with nulls replaced:\")\n",
"display(df.fillna(1))\n",
"\n",
"# Sort df based on column of interest\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe sorted based on column:\")\n",
"df_sorted = df.sort_values('bill_length_mm')\n",
"display(df_sorted)\n",
"\n",
"# Resetting the index to the new order after sorting\n",
"df_sorted_reset = df_sorted.reset_index(drop=True)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame with reset index:\")\n",
"display(df_sorted_reset)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"Reset Index Function Documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/docs/reference/api/pandas.DataFrame.reset_index.html"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Inplace vs. Not Inplace\n",
"\n",
"tester = df_sorted.copy()\n",
"# Resetting the index to the new order after sorting not inplace\n",
"print(\"DataFrame with reset index not inplace:\")\n",
"display(tester.reset_index(drop=True))\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nOriginal Dataframe:\")\n",
"display(tester)\n",
"\n",
"# Resetting the index to the new order after sorting inplace\n",
"print(\"DataFrame with reset index inplace:\")\n",
"tester.reset_index(drop=True,inplace=True)\n",
"display(tester)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"#Another common example dataset\n",
"iris = sns.load_dataset(\"iris\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
" "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercises 1\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Display the first and then the last 15 rows in a dataframe \n",
"print('First 15 rows:')\n",
"display(iris.head(15))\n",
"print('\\nLast 15 rows:')\n",
"display(iris.tail(15))\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Use any function to explore the new dataset\n",
"print('\\nIris Description:')\n",
"display(iris.describe())\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Display only the sepal_length column in the format of a pandas dataframe\n",
"print('\\nSepal_length column as a dataframe:')\n",
"display(iris[['sepal_length']])\n",
"\n",
"type_df = type(iris[['sepal_length']])\n",
"print(f'\\nDatatype: {type_df}')\n",
"\n",
"# 4. Display only sepal_length column in the format of a pandas series and check the type\n",
"print('\\nSepal_length column as a series:')\n",
"display(iris['sepal_length'])\n",
"\n",
"type_series = type(iris['sepal_length'])\n",
"print(f'\\nDatatype: {type_series}')\n",
"\n",
"# 5. Get the names of all the species and check the type\n",
"species = iris['species'].unique()\n",
"print(f'\\nSpecies Names: {species}')\n",
"\n",
"# 6. Get the total number of null values in the entire dataFrame\n",
"sum_null = iris.isnull().sum().sum()\n",
"print(f'\\nTotal number of nulls:{sum_null}')\n",
"\n",
"# 7. Replace all null values w/ the mean value of that column (note: operation only works w/ numeric columns)\n",
"col_means = iris.mean()\n",
"print('\\nColumn Means:')\n",
"display(col_means)\n",
"\n",
"print('\\nFilled NA')\n",
"df_filled = iris.fillna(col_means)\n",
"display(df_filled)\n",
"\n",
"# 8. Sort the dataframe in decending order based on a petal_length and reset the index without writing over the original dataframe\n",
"\n",
"df_sorted = iris.sort_values('petal_length', ascending=False)\n",
"print(\"DataFrame with reset index not inplace:\")\n",
"display(df_sorted.reset_index(drop=True))\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nOriginal Dataframe:\")\n",
"display(df_sorted)\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Several different ways to subset/query a dataframe"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### By Column"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Selecting Data from DataFrame\n",
"\n",
"# Understanding Pandas Series\n",
"# 1. A Series is like a single column of data\n",
"# 2. It has an index (labels for each item) but no column names\n",
"# 3. A Series can have a name, which labels the whole Series\n",
"\n",
"print(\"Single column (as Series):\")\n",
"series = df['bill_length_mm']\n",
"display(series)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nSeries index (labels for each item):\")\n",
"print(series.index)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nSeries name:\")\n",
"print(series.name)\n",
"\n",
"# We can change the Series name\n",
"series.name = \"Bill Length\"\n",
"print(\"\\nUpdated Series name:\")\n",
"print(series.name)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Selecting Data from DataFrame Pt. 2\n",
"\n",
"# When we use double brackets, we get a DataFrame instead\n",
"print(\"Single column (as DataFrame):\")\n",
"single_column_df = df[['bill_length_mm']]\n",
"display(single_column_df)\n",
"print(\"Type:\", type(single_column_df))\n",
"\n",
"# Note: A Series is like a single labeled column, while a DataFrame \n",
"# is like a table with potentially many columns. The Series index is \n",
"# like row labels, and its name can become a column name in a DataFrame."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Key Concept: Series vs DataFrame in Column Selection\n",
"* Using double brackets [[]] selects columns and returns a DataFrame\n",
"* Using single brackets [] for a single column returns a Series\n",
"* A DataFrame is a 2D structure with both row and column labels\n",
"* A Series is a 1D structure with only row labels (index)\n",
"\n",
"* Note: Some operations work on Series, others on DataFrames, so it's helpful to know which one you're using."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### How can we visulize the distribution of this single variable better?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Basic Data Visualization\n",
"plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))\n",
"sns.histplot(df['bill_length_mm'], kde=True, bins=20)\n",
"plt.title('Distribution of Bill Length')\n",
"plt.xlabel('Bill Length (mm)')\n",
"plt.ylabel('Count')\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Helpful resources for data visulization in python: \n",
"- https://python-graph-gallery.com\n",
"- https://github.com/cxli233/FriendsDontLetFriends"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### By Row"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Data Selection\n",
"# Select specific rows and columns using iloc (integer-location based indexing)\n",
"print(\"Using iloc:\")\n",
"print(df.iloc[2, 2]) # Value at 3rd row, 3rd column\n",
"\n",
"# Select rows using loc (label-based indexing)\n",
"print(\"\\nUsing loc:\")\n",
"display(df.loc[3]) # 4th row\n",
"display(df.loc[0:3]) # First 4 rows\n",
"\n",
"# Query the DataFrame by condition\n",
"print(\"\\nUsing query:\")\n",
"display(df.query(\"year > 2008\"))\n",
"\n",
"# Query dataframe based on two conditions\n",
"\n",
"# Method 1\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 1 Dataframe:\")\n",
"yr_vec = df['year'] > 2008\n",
"island_vec = df['island'] == 'Biscoe'\n",
"\n",
"combine_vec = np.logical_and(yr_vec,island_vec)\n",
"display(df[combine_vec])\n",
"\n",
"#Method 2\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 2 Dataframe:\")\n",
"display(df[(yr_vec) & (island_vec)])"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercises 2\n",
"\n",
"display(iris.head())\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Get out the sepal_length column as a pandas series and rename the series\n",
"print(\"Sepal_length column (as Series):\")\n",
"sepal_length_series = iris['sepal_length']\n",
"display(sepal_length_series)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nSeries name:\")\n",
"print(sepal_length_series.name)\n",
"\n",
"sepal_length_series.name = \"Sepal Length\"\n",
"print(\"\\nUpdated Series name:\")\n",
"print(sepal_length_series.name)\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Get the 5th row, 2nd column element using the iloc function\n",
"\n",
"element_5_2 = iris.iloc[4, 1]\n",
"print(f\"\\n5th row, 2nd column element: {element_5_2}\")\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Get the last 5 rows using the loc function and then iloc\n",
"num_rows = iris.shape[0]\n",
"print(\"\\nUsing loc function:\")\n",
"display(iris.loc[num_rows-5:num_rows-1]) \n",
"print(\"\\nUsing iloc function:\")\n",
"display(iris.iloc[-5:])\n",
"#Note: The iloc function allows for integer-based indexing, which includes using negative indices to count from the end of the DataFrame\n",
"\n",
"# 4. Visualize the distribution of the sepal length of the iris dataset\n",
"plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))\n",
"sns.histplot(iris['sepal_length'], kde=True, bins=20)\n",
"plt.title('Distribution of Sepal Length')\n",
"plt.xlabel('Sepal Length')\n",
"plt.ylabel('Count')\n",
"plt.show()\n",
"\n",
"# 5. Display only the rows that have a petal length greater than or equal to 1.5 and petal width greater than or equal to 0.5\n",
"\n",
"# Method 1\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 1 Dataframe And Logic:\")\n",
"petal_length_bool = iris['petal_length'] >= 1.5\n",
"petal_width_bool = iris['petal_width'] >= 0.5\n",
"\n",
"combine_bool = np.logical_and(petal_length_bool,petal_width_bool)\n",
"display(iris[combine_bool])\n",
"\n",
"#Method 2\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 2 Dataframe And Logic:\")\n",
"display(iris[(petal_length_bool) & (petal_width_bool)])\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"# 6. Display only the rows that meet either of two conditions\n",
"\n",
"# Method 1\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 1 Dataframe Or Logic:\")\n",
"combine_bool = np.logical_or(petal_length_bool,petal_width_bool)\n",
"display(iris[combine_bool])\n",
"\n",
"#Method 2\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 2 Dataframe Or Logic:\")\n",
"display(iris[(petal_length_bool) | (petal_width_bool)])\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Histograms allowed us to visualize the distribution of a singel feature, what about the relation between features? How do we decide our filtering condition with multiple features?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Create jointplots to determine relationships between specific variables\n",
"sns.jointplot(data=df, x=\"bill_length_mm\", y=\"bill_depth_mm\")\n",
"plt.show()\n",
"\n",
"sns.jointplot(data=df, x=\"body_mass_g\", y=\"flipper_length_mm\")\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Create pairplots to determine relationships between all numeric variables\n",
"sns.pairplot(df)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Different ways of visualizing the same data can lead to different interpretations\n",
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
"fig , ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(15,12), ncols=2,nrows=2)\n",
"sns.swarmplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[0,0],hue='species')\n",
"sns.violinplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[0,1])\n",
"sns.boxplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[1,0])\n",
"sns.barplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[1,1])\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercise 3\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Plot relation petal length and petal width\n",
"print('Joint plot of petal length and petal width')\n",
"sns.jointplot(data=iris, x=\"petal_length\", y=\"petal_width\")\n",
"plt.show()\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Plot relationship between all numeric values\n",
"print('\\nPairplot of all numercic values')\n",
"sns.pairplot(iris)\n",
"plt.show()\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Use two different plots to visualize the data for petal length for only the setosa and virginica species\n",
"print('\\nTwo different plots to visualize petal length for only the setosa and virginica species')\n",
"iris_subset = iris[(iris['species'] == 'setosa') | (iris['species'] == 'virginica')]\n",
"fig , ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12,7), ncols=2,nrows=1)\n",
"sns.violinplot(data=iris_subset,x='species',y='petal_length',ax=ax[0])\n",
"sns.barplot(data=iris_subset,x='species',y='petal_length',ax=ax[1])\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### After editing our dataframes how can we save them in a way that allows us to read them back in without having to redo our analysis?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Saving Pandas Dataframes\n",
"\n",
"df.to_csv('penguins.csv', index=False)\n",
"\n",
"df.to_excel('penguins.xlsx', index=False, sheet_name='Sheet1')"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Reading Pandas Dataframes\n",
"\n",
"df_csv = pd.read_csv('penguins.csv')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from CSV:\")\n",
"display(df_csv)\n",
"\n",
"df_excel = pd.read_excel('penguins.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet1')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from Excel:\")\n",
"display(df_excel)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercise 4\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Write the iris dataset to a csv\n",
"iris.to_csv('iris.csv', index=False)\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Write the iris dataset to a excel\n",
"iris.to_excel('iris.xlsx', index=False, sheet_name='Sheet1')\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Read in the iris dataset from the csv\n",
"iris_csv = pd.read_csv('iris.csv')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from CSV:\")\n",
"display(iris_csv)\n",
"\n",
"# 4. Read in the iris dataset from the excel\n",
"iris_excel = pd.read_excel('iris.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet1')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from Excel:\")\n",
"display(iris_excel)\n",
"\n",
"# 5. Write to a file w semicolon as a seperator\n",
"iris.to_csv('iris_semicolon.csv', index=False, sep=';')\n",
"\n",
"# 6. Read in the semicolon file\n",
"iris_semicolon_csv = pd.read_csv('iris_semicolon.csv', sep=';')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from semicolon CSV:\")\n",
"display(iris_semicolon_csv)\n"
]
}
],
"metadata": {
"kernelspec": {
"display_name": "Python 3 (ipykernel)",
"language": "python",
"name": "python3"
},
"language_info": {
"codemirror_mode": {
"name": "ipython",
"version": 3
},
"file_extension": ".py",
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
"name": "python",
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
"version": "3.9.-1"
}
},
"nbformat": 4,
"nbformat_minor": 4
}
"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercises 1\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Display the first and then the last 15 rows in a dataframe \n",
"print('First 15 rows:')\n",
"display(iris.head(15))\n",
"print('\\nLast 15 rows:')\n",
"display(iris.tail(15))\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Use any function to explore the new dataset\n",
"print('\\nIris Description:')\n",
"display(iris.describe())\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Display only the sepal_length column in the format of a pandas dataframe\n",
"print('\\nSepal_length column as a dataframe:')\n",
"display(iris[['sepal_length']])\n",
"\n",
"type_df = type(iris[['sepal_length']])\n",
"print(f'\\nDatatype: {type_df}')\n",
"\n",
"# 4. Display only sepal_length column in the format of a pandas series and check the type\n",
"print('\\nSepal_length column as a series:')\n",
"display(iris['sepal_length'])\n",
"\n",
"type_series = type(iris['sepal_length'])\n",
"print(f'\\nDatatype: {type_series}')\n",
"\n",
"# 5. Get the names of all the species and check the type\n",
"species = iris['species'].unique()\n",
"print(f'\\nSpecies Names: {species}')\n",
"\n",
"# 6. Get the total number of null values in the entire dataFrame\n",
"sum_null = iris.isnull().sum().sum()\n",
"print(f'\\nTotal number of nulls:{sum_null}')\n",
"\n",
"# 7. Replace all null values w/ the mean value of that column (note: operation only works w/ numeric columns)\n",
"col_means = iris.mean()\n",
"print('\\nColumn Means:')\n",
"display(col_means)\n",
"\n",
"print('\\nFilled NA')\n",
"df_filled = iris.fillna(col_means)\n",
"display(df_filled)\n",
"\n",
"# 8. Sort the dataframe in decending order based on a petal_length and reset the index without writing over the original dataframe\n",
"\n",
"df_sorted = iris.sort_values('petal_length', ascending=False)\n",
"print(\"DataFrame with reset index not inplace:\")\n",
"display(df_sorted.reset_index(drop=True))\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nOriginal Dataframe:\")\n",
"display(df_sorted)\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Several different ways to subset/query a dataframe"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### By Column"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Selecting Data from DataFrame\n",
"\n",
"# Understanding Pandas Series\n",
"# 1. A Series is like a single column of data\n",
"# 2. It has an index (labels for each item) but no column names\n",
"# 3. A Series can have a name, which labels the whole Series\n",
"\n",
"print(\"Single column (as Series):\")\n",
"series = df['bill_length_mm']\n",
"display(series)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nSeries index (labels for each item):\")\n",
"print(series.index)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nSeries name:\")\n",
"print(series.name)\n",
"\n",
"# We can change the Series name\n",
"series.name = \"Bill Length\"\n",
"print(\"\\nUpdated Series name:\")\n",
"print(series.name)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Selecting Data from DataFrame Pt. 2\n",
"\n",
"# When we use double brackets, we get a DataFrame instead\n",
"print(\"Single column (as DataFrame):\")\n",
"single_column_df = df[['bill_length_mm']]\n",
"display(single_column_df)\n",
"print(\"Type:\", type(single_column_df))\n",
"\n",
"# Note: A Series is like a single labeled column, while a DataFrame \n",
"# is like a table with potentially many columns. The Series index is \n",
"# like row labels, and its name can become a column name in a DataFrame."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Key Concept: Series vs DataFrame in Column Selection\n",
"* Using double brackets [[]] selects columns and returns a DataFrame\n",
"* Using single brackets [] for a single column returns a Series\n",
"* A DataFrame is a 2D structure with both row and column labels\n",
"* A Series is a 1D structure with only row labels (index)\n",
"\n",
"* Note: Some operations work on Series, others on DataFrames, so it's helpful to know which one you're using."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### How can we visulize the distribution of this single variable better?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Basic Data Visualization\n",
"plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))\n",
"sns.histplot(df['bill_length_mm'], kde=True, bins=20)\n",
"plt.title('Distribution of Bill Length')\n",
"plt.xlabel('Bill Length (mm)')\n",
"plt.ylabel('Count')\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Helpful resources for data visulization in python: \n",
"- https://python-graph-gallery.com\n",
"- https://github.com/cxli233/FriendsDontLetFriends"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### By Row"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Data Selection\n",
"# Select specific rows and columns using iloc (integer-location based indexing)\n",
"print(\"Using iloc:\")\n",
"print(df.iloc[2, 2]) # Value at 3rd row, 3rd column\n",
"\n",
"# Select rows using loc (label-based indexing)\n",
"print(\"\\nUsing loc:\")\n",
"display(df.loc[3]) # 4th row\n",
"display(df.loc[0:3]) # First 4 rows\n",
"\n",
"# Query the DataFrame by condition\n",
"print(\"\\nUsing query:\")\n",
"display(df.query(\"year > 2008\"))\n",
"\n",
"# Query dataframe based on two conditions\n",
"\n",
"# Method 1\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 1 Dataframe:\")\n",
"yr_vec = df['year'] > 2008\n",
"island_vec = df['island'] == 'Biscoe'\n",
"\n",
"combine_vec = np.logical_and(yr_vec,island_vec)\n",
"display(df[combine_vec])\n",
"\n",
"#Method 2\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 2 Dataframe:\")\n",
"display(df[(yr_vec) & (island_vec)])"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercises 2\n",
"\n",
"display(iris.head())\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Get out the sepal_length column as a pandas series and rename the series\n",
"print(\"Sepal_length column (as Series):\")\n",
"sepal_length_series = iris['sepal_length']\n",
"display(sepal_length_series)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nSeries name:\")\n",
"print(sepal_length_series.name)\n",
"\n",
"sepal_length_series.name = \"Sepal Length\"\n",
"print(\"\\nUpdated Series name:\")\n",
"print(sepal_length_series.name)\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Get the 5th row, 2nd column element using the iloc function\n",
"\n",
"element_5_2 = iris.iloc[4, 1]\n",
"print(f\"\\n5th row, 2nd column element: {element_5_2}\")\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Get the last 5 rows using the loc function and then iloc\n",
"num_rows = iris.shape[0]\n",
"print(\"\\nUsing loc function:\")\n",
"display(iris.loc[num_rows-5:num_rows-1]) \n",
"print(\"\\nUsing iloc function:\")\n",
"display(iris.iloc[-5:])\n",
"#Note: The iloc function allows for integer-based indexing, which includes using negative indices to count from the end of the DataFrame\n",
"\n",
"# 4. Visualize the distribution of the sepal length of the iris dataset\n",
"plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))\n",
"sns.histplot(iris['sepal_length'], kde=True, bins=20)\n",
"plt.title('Distribution of Sepal Length')\n",
"plt.xlabel('Sepal Length')\n",
"plt.ylabel('Count')\n",
"plt.show()\n",
"\n",
"# 5. Display only the rows that have a petal length greater than or equal to 1.5 and petal width greater than or equal to 0.5\n",
"\n",
"# Method 1\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 1 Dataframe And Logic:\")\n",
"petal_length_bool = iris['petal_length'] >= 1.5\n",
"petal_width_bool = iris['petal_width'] >= 0.5\n",
"\n",
"combine_bool = np.logical_and(petal_length_bool,petal_width_bool)\n",
"display(iris[combine_bool])\n",
"\n",
"#Method 2\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 2 Dataframe And Logic:\")\n",
"display(iris[(petal_length_bool) & (petal_width_bool)])\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"# 6. Display only the rows that meet either of two conditions\n",
"\n",
"# Method 1\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 1 Dataframe Or Logic:\")\n",
"combine_bool = np.logical_or(petal_length_bool,petal_width_bool)\n",
"display(iris[combine_bool])\n",
"\n",
"#Method 2\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 2 Dataframe Or Logic:\")\n",
"display(iris[(petal_length_bool) | (petal_width_bool)])\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Histograms allowed us to visualize the distribution of a singel feature, what about the relation between features? How do we decide our filtering condition with multiple features?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Create jointplots to determine relationships between specific variables\n",
"sns.jointplot(data=df, x=\"bill_length_mm\", y=\"bill_depth_mm\")\n",
"plt.show()\n",
"\n",
"sns.jointplot(data=df, x=\"body_mass_g\", y=\"flipper_length_mm\")\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Create pairplots to determine relationships between all numeric variables\n",
"sns.pairplot(df)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Different ways of visualizing the same data can lead to different interpretations\n",
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
"fig , ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(15,12), ncols=2,nrows=2)\n",
"sns.swarmplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[0,0],hue='species')\n",
"sns.violinplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[0,1])\n",
"sns.boxplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[1,0])\n",
"sns.barplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[1,1])\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercise 3\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Plot relation petal length and petal width\n",
"print('Joint plot of petal length and petal width')\n",
"sns.jointplot(data=iris, x=\"petal_length\", y=\"petal_width\")\n",
"plt.show()\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Plot relationship between all numeric values\n",
"print('\\nPairplot of all numercic values')\n",
"sns.pairplot(iris)\n",
"plt.show()\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Use two different plots to visualize the data for petal length for only the setosa and virginica species\n",
"print('\\nTwo different plots to visualize petal length for only the setosa and virginica species')\n",
"iris_subset = iris[(iris['species'] == 'setosa') | (iris['species'] == 'virginica')]\n",
"fig , ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12,7), ncols=2,nrows=1)\n",
"sns.violinplot(data=iris_subset,x='species',y='petal_length',ax=ax[0])\n",
"sns.barplot(data=iris_subset,x='species',y='petal_length',ax=ax[1])\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### After editing our dataframes how can we save them in a way that allows us to read them back in without having to redo our analysis?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Saving Pandas Dataframes\n",
"\n",
"df.to_csv('penguins.csv', index=False)\n",
"\n",
"df.to_excel('penguins.xlsx', index=False, sheet_name='Sheet1')"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Reading Pandas Dataframes\n",
"\n",
"df_csv = pd.read_csv('penguins.csv')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from CSV:\")\n",
"display(df_csv)\n",
"\n",
"df_excel = pd.read_excel('penguins.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet1')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from Excel:\")\n",
"display(df_excel)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercise 4\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Write the iris dataset to a csv\n",
"iris.to_csv('iris.csv', index=False)\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Write the iris dataset to a excel\n",
"iris.to_excel('iris.xlsx', index=False, sheet_name='Sheet1')\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Read in the iris dataset from the csv\n",
"iris_csv = pd.read_csv('iris.csv')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from CSV:\")\n",
"display(iris_csv)\n",
"\n",
"# 4. Read in the iris dataset from the excel\n",
"iris_excel = pd.read_excel('iris.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet1')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from Excel:\")\n",
"display(iris_excel)\n",
"\n",
"# 5. Write to a file w semicolon as a seperator\n",
"iris.to_csv('iris_semicolon.csv', index=False, sep=';')\n",
"\n",
"# 6. Read in the semicolon file\n",
"iris_semicolon_csv = pd.read_csv('iris_semicolon.csv', sep=';')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from semicolon CSV:\")\n",
"display(iris_semicolon_csv)\n"
]
}
],
"metadata": {
"kernelspec": {
"display_name": "Python 3 (ipykernel)",
"language": "python",
"name": "python3"
},
"language_info": {
"codemirror_mode": {
"name": "ipython",
"version": 3
},
"file_extension": ".py",
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
"name": "python",
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
"version": "3.9.-1"
}
},
"nbformat": 4,
"nbformat_minor": 4
}
 \n",
"
\n",
" "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Introduction"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"Pandas is a library for working with tabular data. It was orignally based on the R data.frame library. \n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Loading and Displaying the Dataset\n",
"import pandas as pd\n",
"import seaborn as sns\n",
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
"import numpy as np\n",
"\n",
"from palmerpenguins import load_penguins\n",
"df = load_penguins()\n",
"\n",
"print(\"Type of the dataset:\", type(df))\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame using head command:\")\n",
"display(df.head())\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame using tail command:\")\n",
"display(df.tail())"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Key Concepts:\n",
"\n",
"- A DataFrame is a 2-dimensional data structure in pandas. It's like a spreadsheet or a table with rows and columns.\n",
"- Generally, \n",
" - Columns represent features (variables we measure or observe)\n",
" - Rows represent individual observations (in this case, each penguin)\n",
"\n",
"- In this dataset:\n",
" - Each row represents a single penguin\n",
" - Each column represents a feature (e.g., species, island, bill length)\n",
"\n",
"- Common functions for initial data exploration:\n",
" - df.head() Shows the first 5 rows by default\n",
" - df.info() Provides a concise summary of the DataFrame\n",
" - df.describe() Generates descriptive statistics for numerical columns"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Whole DataFrame Exploration\n",
"print(\"Summary statistics:\")\n",
"display(df.describe())\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nData types of columns:\")\n",
"display(df.dtypes)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nColumn names:\")\n",
"print(df.columns)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame info:\")\n",
"df.info()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Column Specific Operations\n",
"\n",
"# Using value counts to get the number of penguins for each species\n",
"species_counts = df['species'].value_counts()\n",
"print(\"Penguins per species:\")\n",
"print(species_counts)\n",
"\n",
"# Get the mean bill length\n",
"bill_length = df['bill_length_mm'].mean() # Can get the mode and sum\n",
"print(f'\\nAverage bill length: {bill_length}')\n",
"\n",
"# Get the mean bill length per species\n",
"species_bill_length = df.groupby('species')['bill_length_mm'].mean()\n",
"print(\"\\nAverage bill length per species:\")\n",
"print(species_bill_length)\n",
"\n",
"# Get the unique species\n",
"unique_species = df['species'].unique()\n",
"print(f\"\\nUnique species: {unique_species}\")\n",
"\n",
"# Get number of null values\n",
"boolean_vec = df.isnull()\n",
"print(f\"\\nBoolean_vec: {boolean_vec}\")\n",
"sum = boolean_vec.sum()\n",
"print(f\"\\nBoolean_vec sum: {sum}\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Data Cleaning\n",
"\n",
"# Examine original dataframe\n",
"print(\"Orifinal dataframe:\")\n",
"display(df)\n",
"\n",
"# Drop all rows with a null value\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe with non-null rows:\")\n",
"display(df.dropna())\n",
"\n",
"# Drop all columns with a null value\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe with non-null columns:\")\n",
"display(df.dropna(axis=1))\n",
"\n",
"# Replace all null values\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe with nulls replaced:\")\n",
"display(df.fillna(1))\n",
"\n",
"# Sort df based on column of interest\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe sorted based on column:\")\n",
"df_sorted = df.sort_values('bill_length_mm')\n",
"display(df_sorted)\n",
"\n",
"# Resetting the index to the new order after sorting\n",
"df_sorted_reset = df_sorted.reset_index(drop=True)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame with reset index:\")\n",
"display(df_sorted_reset)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"Reset Index Function Documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/docs/reference/api/pandas.DataFrame.reset_index.html"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Inplace vs. Not Inplace\n",
"\n",
"tester = df_sorted.copy()\n",
"# Resetting the index to the new order after sorting not inplace\n",
"print(\"DataFrame with reset index not inplace:\")\n",
"display(tester.reset_index(drop=True))\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nOriginal Dataframe:\")\n",
"display(tester)\n",
"\n",
"# Resetting the index to the new order after sorting inplace\n",
"print(\"DataFrame with reset index inplace:\")\n",
"tester.reset_index(drop=True,inplace=True)\n",
"display(tester)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"#Another common example dataset\n",
"iris = sns.load_dataset(\"iris\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"
"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Introduction"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"Pandas is a library for working with tabular data. It was orignally based on the R data.frame library. \n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Loading and Displaying the Dataset\n",
"import pandas as pd\n",
"import seaborn as sns\n",
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
"import numpy as np\n",
"\n",
"from palmerpenguins import load_penguins\n",
"df = load_penguins()\n",
"\n",
"print(\"Type of the dataset:\", type(df))\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame using head command:\")\n",
"display(df.head())\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame using tail command:\")\n",
"display(df.tail())"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Key Concepts:\n",
"\n",
"- A DataFrame is a 2-dimensional data structure in pandas. It's like a spreadsheet or a table with rows and columns.\n",
"- Generally, \n",
" - Columns represent features (variables we measure or observe)\n",
" - Rows represent individual observations (in this case, each penguin)\n",
"\n",
"- In this dataset:\n",
" - Each row represents a single penguin\n",
" - Each column represents a feature (e.g., species, island, bill length)\n",
"\n",
"- Common functions for initial data exploration:\n",
" - df.head() Shows the first 5 rows by default\n",
" - df.info() Provides a concise summary of the DataFrame\n",
" - df.describe() Generates descriptive statistics for numerical columns"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Whole DataFrame Exploration\n",
"print(\"Summary statistics:\")\n",
"display(df.describe())\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nData types of columns:\")\n",
"display(df.dtypes)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nColumn names:\")\n",
"print(df.columns)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame info:\")\n",
"df.info()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Column Specific Operations\n",
"\n",
"# Using value counts to get the number of penguins for each species\n",
"species_counts = df['species'].value_counts()\n",
"print(\"Penguins per species:\")\n",
"print(species_counts)\n",
"\n",
"# Get the mean bill length\n",
"bill_length = df['bill_length_mm'].mean() # Can get the mode and sum\n",
"print(f'\\nAverage bill length: {bill_length}')\n",
"\n",
"# Get the mean bill length per species\n",
"species_bill_length = df.groupby('species')['bill_length_mm'].mean()\n",
"print(\"\\nAverage bill length per species:\")\n",
"print(species_bill_length)\n",
"\n",
"# Get the unique species\n",
"unique_species = df['species'].unique()\n",
"print(f\"\\nUnique species: {unique_species}\")\n",
"\n",
"# Get number of null values\n",
"boolean_vec = df.isnull()\n",
"print(f\"\\nBoolean_vec: {boolean_vec}\")\n",
"sum = boolean_vec.sum()\n",
"print(f\"\\nBoolean_vec sum: {sum}\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Data Cleaning\n",
"\n",
"# Examine original dataframe\n",
"print(\"Orifinal dataframe:\")\n",
"display(df)\n",
"\n",
"# Drop all rows with a null value\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe with non-null rows:\")\n",
"display(df.dropna())\n",
"\n",
"# Drop all columns with a null value\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe with non-null columns:\")\n",
"display(df.dropna(axis=1))\n",
"\n",
"# Replace all null values\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe with nulls replaced:\")\n",
"display(df.fillna(1))\n",
"\n",
"# Sort df based on column of interest\n",
"print(\"\\nDataframe sorted based on column:\")\n",
"df_sorted = df.sort_values('bill_length_mm')\n",
"display(df_sorted)\n",
"\n",
"# Resetting the index to the new order after sorting\n",
"df_sorted_reset = df_sorted.reset_index(drop=True)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nDataFrame with reset index:\")\n",
"display(df_sorted_reset)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"Reset Index Function Documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/docs/reference/api/pandas.DataFrame.reset_index.html"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Inplace vs. Not Inplace\n",
"\n",
"tester = df_sorted.copy()\n",
"# Resetting the index to the new order after sorting not inplace\n",
"print(\"DataFrame with reset index not inplace:\")\n",
"display(tester.reset_index(drop=True))\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nOriginal Dataframe:\")\n",
"display(tester)\n",
"\n",
"# Resetting the index to the new order after sorting inplace\n",
"print(\"DataFrame with reset index inplace:\")\n",
"tester.reset_index(drop=True,inplace=True)\n",
"display(tester)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"#Another common example dataset\n",
"iris = sns.load_dataset(\"iris\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
" "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercises 1\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Display the first and then the last 15 rows in a dataframe \n",
"print('First 15 rows:')\n",
"display(iris.head(15))\n",
"print('\\nLast 15 rows:')\n",
"display(iris.tail(15))\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Use any function to explore the new dataset\n",
"print('\\nIris Description:')\n",
"display(iris.describe())\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Display only the sepal_length column in the format of a pandas dataframe\n",
"print('\\nSepal_length column as a dataframe:')\n",
"display(iris[['sepal_length']])\n",
"\n",
"type_df = type(iris[['sepal_length']])\n",
"print(f'\\nDatatype: {type_df}')\n",
"\n",
"# 4. Display only sepal_length column in the format of a pandas series and check the type\n",
"print('\\nSepal_length column as a series:')\n",
"display(iris['sepal_length'])\n",
"\n",
"type_series = type(iris['sepal_length'])\n",
"print(f'\\nDatatype: {type_series}')\n",
"\n",
"# 5. Get the names of all the species and check the type\n",
"species = iris['species'].unique()\n",
"print(f'\\nSpecies Names: {species}')\n",
"\n",
"# 6. Get the total number of null values in the entire dataFrame\n",
"sum_null = iris.isnull().sum().sum()\n",
"print(f'\\nTotal number of nulls:{sum_null}')\n",
"\n",
"# 7. Replace all null values w/ the mean value of that column (note: operation only works w/ numeric columns)\n",
"col_means = iris.mean()\n",
"print('\\nColumn Means:')\n",
"display(col_means)\n",
"\n",
"print('\\nFilled NA')\n",
"df_filled = iris.fillna(col_means)\n",
"display(df_filled)\n",
"\n",
"# 8. Sort the dataframe in decending order based on a petal_length and reset the index without writing over the original dataframe\n",
"\n",
"df_sorted = iris.sort_values('petal_length', ascending=False)\n",
"print(\"DataFrame with reset index not inplace:\")\n",
"display(df_sorted.reset_index(drop=True))\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nOriginal Dataframe:\")\n",
"display(df_sorted)\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Several different ways to subset/query a dataframe"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### By Column"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Selecting Data from DataFrame\n",
"\n",
"# Understanding Pandas Series\n",
"# 1. A Series is like a single column of data\n",
"# 2. It has an index (labels for each item) but no column names\n",
"# 3. A Series can have a name, which labels the whole Series\n",
"\n",
"print(\"Single column (as Series):\")\n",
"series = df['bill_length_mm']\n",
"display(series)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nSeries index (labels for each item):\")\n",
"print(series.index)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nSeries name:\")\n",
"print(series.name)\n",
"\n",
"# We can change the Series name\n",
"series.name = \"Bill Length\"\n",
"print(\"\\nUpdated Series name:\")\n",
"print(series.name)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Selecting Data from DataFrame Pt. 2\n",
"\n",
"# When we use double brackets, we get a DataFrame instead\n",
"print(\"Single column (as DataFrame):\")\n",
"single_column_df = df[['bill_length_mm']]\n",
"display(single_column_df)\n",
"print(\"Type:\", type(single_column_df))\n",
"\n",
"# Note: A Series is like a single labeled column, while a DataFrame \n",
"# is like a table with potentially many columns. The Series index is \n",
"# like row labels, and its name can become a column name in a DataFrame."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Key Concept: Series vs DataFrame in Column Selection\n",
"* Using double brackets [[]] selects columns and returns a DataFrame\n",
"* Using single brackets [] for a single column returns a Series\n",
"* A DataFrame is a 2D structure with both row and column labels\n",
"* A Series is a 1D structure with only row labels (index)\n",
"\n",
"* Note: Some operations work on Series, others on DataFrames, so it's helpful to know which one you're using."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### How can we visulize the distribution of this single variable better?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Basic Data Visualization\n",
"plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))\n",
"sns.histplot(df['bill_length_mm'], kde=True, bins=20)\n",
"plt.title('Distribution of Bill Length')\n",
"plt.xlabel('Bill Length (mm)')\n",
"plt.ylabel('Count')\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Helpful resources for data visulization in python: \n",
"- https://python-graph-gallery.com\n",
"- https://github.com/cxli233/FriendsDontLetFriends"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### By Row"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Data Selection\n",
"# Select specific rows and columns using iloc (integer-location based indexing)\n",
"print(\"Using iloc:\")\n",
"print(df.iloc[2, 2]) # Value at 3rd row, 3rd column\n",
"\n",
"# Select rows using loc (label-based indexing)\n",
"print(\"\\nUsing loc:\")\n",
"display(df.loc[3]) # 4th row\n",
"display(df.loc[0:3]) # First 4 rows\n",
"\n",
"# Query the DataFrame by condition\n",
"print(\"\\nUsing query:\")\n",
"display(df.query(\"year > 2008\"))\n",
"\n",
"# Query dataframe based on two conditions\n",
"\n",
"# Method 1\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 1 Dataframe:\")\n",
"yr_vec = df['year'] > 2008\n",
"island_vec = df['island'] == 'Biscoe'\n",
"\n",
"combine_vec = np.logical_and(yr_vec,island_vec)\n",
"display(df[combine_vec])\n",
"\n",
"#Method 2\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 2 Dataframe:\")\n",
"display(df[(yr_vec) & (island_vec)])"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercises 2\n",
"\n",
"display(iris.head())\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Get out the sepal_length column as a pandas series and rename the series\n",
"print(\"Sepal_length column (as Series):\")\n",
"sepal_length_series = iris['sepal_length']\n",
"display(sepal_length_series)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nSeries name:\")\n",
"print(sepal_length_series.name)\n",
"\n",
"sepal_length_series.name = \"Sepal Length\"\n",
"print(\"\\nUpdated Series name:\")\n",
"print(sepal_length_series.name)\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Get the 5th row, 2nd column element using the iloc function\n",
"\n",
"element_5_2 = iris.iloc[4, 1]\n",
"print(f\"\\n5th row, 2nd column element: {element_5_2}\")\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Get the last 5 rows using the loc function and then iloc\n",
"num_rows = iris.shape[0]\n",
"print(\"\\nUsing loc function:\")\n",
"display(iris.loc[num_rows-5:num_rows-1]) \n",
"print(\"\\nUsing iloc function:\")\n",
"display(iris.iloc[-5:])\n",
"#Note: The iloc function allows for integer-based indexing, which includes using negative indices to count from the end of the DataFrame\n",
"\n",
"# 4. Visualize the distribution of the sepal length of the iris dataset\n",
"plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))\n",
"sns.histplot(iris['sepal_length'], kde=True, bins=20)\n",
"plt.title('Distribution of Sepal Length')\n",
"plt.xlabel('Sepal Length')\n",
"plt.ylabel('Count')\n",
"plt.show()\n",
"\n",
"# 5. Display only the rows that have a petal length greater than or equal to 1.5 and petal width greater than or equal to 0.5\n",
"\n",
"# Method 1\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 1 Dataframe And Logic:\")\n",
"petal_length_bool = iris['petal_length'] >= 1.5\n",
"petal_width_bool = iris['petal_width'] >= 0.5\n",
"\n",
"combine_bool = np.logical_and(petal_length_bool,petal_width_bool)\n",
"display(iris[combine_bool])\n",
"\n",
"#Method 2\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 2 Dataframe And Logic:\")\n",
"display(iris[(petal_length_bool) & (petal_width_bool)])\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"# 6. Display only the rows that meet either of two conditions\n",
"\n",
"# Method 1\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 1 Dataframe Or Logic:\")\n",
"combine_bool = np.logical_or(petal_length_bool,petal_width_bool)\n",
"display(iris[combine_bool])\n",
"\n",
"#Method 2\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 2 Dataframe Or Logic:\")\n",
"display(iris[(petal_length_bool) | (petal_width_bool)])\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Histograms allowed us to visualize the distribution of a singel feature, what about the relation between features? How do we decide our filtering condition with multiple features?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Create jointplots to determine relationships between specific variables\n",
"sns.jointplot(data=df, x=\"bill_length_mm\", y=\"bill_depth_mm\")\n",
"plt.show()\n",
"\n",
"sns.jointplot(data=df, x=\"body_mass_g\", y=\"flipper_length_mm\")\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Create pairplots to determine relationships between all numeric variables\n",
"sns.pairplot(df)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Different ways of visualizing the same data can lead to different interpretations\n",
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
"fig , ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(15,12), ncols=2,nrows=2)\n",
"sns.swarmplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[0,0],hue='species')\n",
"sns.violinplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[0,1])\n",
"sns.boxplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[1,0])\n",
"sns.barplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[1,1])\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercise 3\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Plot relation petal length and petal width\n",
"print('Joint plot of petal length and petal width')\n",
"sns.jointplot(data=iris, x=\"petal_length\", y=\"petal_width\")\n",
"plt.show()\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Plot relationship between all numeric values\n",
"print('\\nPairplot of all numercic values')\n",
"sns.pairplot(iris)\n",
"plt.show()\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Use two different plots to visualize the data for petal length for only the setosa and virginica species\n",
"print('\\nTwo different plots to visualize petal length for only the setosa and virginica species')\n",
"iris_subset = iris[(iris['species'] == 'setosa') | (iris['species'] == 'virginica')]\n",
"fig , ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12,7), ncols=2,nrows=1)\n",
"sns.violinplot(data=iris_subset,x='species',y='petal_length',ax=ax[0])\n",
"sns.barplot(data=iris_subset,x='species',y='petal_length',ax=ax[1])\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### After editing our dataframes how can we save them in a way that allows us to read them back in without having to redo our analysis?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Saving Pandas Dataframes\n",
"\n",
"df.to_csv('penguins.csv', index=False)\n",
"\n",
"df.to_excel('penguins.xlsx', index=False, sheet_name='Sheet1')"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Reading Pandas Dataframes\n",
"\n",
"df_csv = pd.read_csv('penguins.csv')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from CSV:\")\n",
"display(df_csv)\n",
"\n",
"df_excel = pd.read_excel('penguins.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet1')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from Excel:\")\n",
"display(df_excel)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercise 4\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Write the iris dataset to a csv\n",
"iris.to_csv('iris.csv', index=False)\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Write the iris dataset to a excel\n",
"iris.to_excel('iris.xlsx', index=False, sheet_name='Sheet1')\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Read in the iris dataset from the csv\n",
"iris_csv = pd.read_csv('iris.csv')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from CSV:\")\n",
"display(iris_csv)\n",
"\n",
"# 4. Read in the iris dataset from the excel\n",
"iris_excel = pd.read_excel('iris.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet1')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from Excel:\")\n",
"display(iris_excel)\n",
"\n",
"# 5. Write to a file w semicolon as a seperator\n",
"iris.to_csv('iris_semicolon.csv', index=False, sep=';')\n",
"\n",
"# 6. Read in the semicolon file\n",
"iris_semicolon_csv = pd.read_csv('iris_semicolon.csv', sep=';')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from semicolon CSV:\")\n",
"display(iris_semicolon_csv)\n"
]
}
],
"metadata": {
"kernelspec": {
"display_name": "Python 3 (ipykernel)",
"language": "python",
"name": "python3"
},
"language_info": {
"codemirror_mode": {
"name": "ipython",
"version": 3
},
"file_extension": ".py",
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
"name": "python",
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
"version": "3.9.-1"
}
},
"nbformat": 4,
"nbformat_minor": 4
}
"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercises 1\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Display the first and then the last 15 rows in a dataframe \n",
"print('First 15 rows:')\n",
"display(iris.head(15))\n",
"print('\\nLast 15 rows:')\n",
"display(iris.tail(15))\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Use any function to explore the new dataset\n",
"print('\\nIris Description:')\n",
"display(iris.describe())\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Display only the sepal_length column in the format of a pandas dataframe\n",
"print('\\nSepal_length column as a dataframe:')\n",
"display(iris[['sepal_length']])\n",
"\n",
"type_df = type(iris[['sepal_length']])\n",
"print(f'\\nDatatype: {type_df}')\n",
"\n",
"# 4. Display only sepal_length column in the format of a pandas series and check the type\n",
"print('\\nSepal_length column as a series:')\n",
"display(iris['sepal_length'])\n",
"\n",
"type_series = type(iris['sepal_length'])\n",
"print(f'\\nDatatype: {type_series}')\n",
"\n",
"# 5. Get the names of all the species and check the type\n",
"species = iris['species'].unique()\n",
"print(f'\\nSpecies Names: {species}')\n",
"\n",
"# 6. Get the total number of null values in the entire dataFrame\n",
"sum_null = iris.isnull().sum().sum()\n",
"print(f'\\nTotal number of nulls:{sum_null}')\n",
"\n",
"# 7. Replace all null values w/ the mean value of that column (note: operation only works w/ numeric columns)\n",
"col_means = iris.mean()\n",
"print('\\nColumn Means:')\n",
"display(col_means)\n",
"\n",
"print('\\nFilled NA')\n",
"df_filled = iris.fillna(col_means)\n",
"display(df_filled)\n",
"\n",
"# 8. Sort the dataframe in decending order based on a petal_length and reset the index without writing over the original dataframe\n",
"\n",
"df_sorted = iris.sort_values('petal_length', ascending=False)\n",
"print(\"DataFrame with reset index not inplace:\")\n",
"display(df_sorted.reset_index(drop=True))\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nOriginal Dataframe:\")\n",
"display(df_sorted)\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Several different ways to subset/query a dataframe"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### By Column"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Selecting Data from DataFrame\n",
"\n",
"# Understanding Pandas Series\n",
"# 1. A Series is like a single column of data\n",
"# 2. It has an index (labels for each item) but no column names\n",
"# 3. A Series can have a name, which labels the whole Series\n",
"\n",
"print(\"Single column (as Series):\")\n",
"series = df['bill_length_mm']\n",
"display(series)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nSeries index (labels for each item):\")\n",
"print(series.index)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nSeries name:\")\n",
"print(series.name)\n",
"\n",
"# We can change the Series name\n",
"series.name = \"Bill Length\"\n",
"print(\"\\nUpdated Series name:\")\n",
"print(series.name)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Selecting Data from DataFrame Pt. 2\n",
"\n",
"# When we use double brackets, we get a DataFrame instead\n",
"print(\"Single column (as DataFrame):\")\n",
"single_column_df = df[['bill_length_mm']]\n",
"display(single_column_df)\n",
"print(\"Type:\", type(single_column_df))\n",
"\n",
"# Note: A Series is like a single labeled column, while a DataFrame \n",
"# is like a table with potentially many columns. The Series index is \n",
"# like row labels, and its name can become a column name in a DataFrame."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Key Concept: Series vs DataFrame in Column Selection\n",
"* Using double brackets [[]] selects columns and returns a DataFrame\n",
"* Using single brackets [] for a single column returns a Series\n",
"* A DataFrame is a 2D structure with both row and column labels\n",
"* A Series is a 1D structure with only row labels (index)\n",
"\n",
"* Note: Some operations work on Series, others on DataFrames, so it's helpful to know which one you're using."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### How can we visulize the distribution of this single variable better?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Basic Data Visualization\n",
"plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))\n",
"sns.histplot(df['bill_length_mm'], kde=True, bins=20)\n",
"plt.title('Distribution of Bill Length')\n",
"plt.xlabel('Bill Length (mm)')\n",
"plt.ylabel('Count')\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Helpful resources for data visulization in python: \n",
"- https://python-graph-gallery.com\n",
"- https://github.com/cxli233/FriendsDontLetFriends"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### By Row"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Data Selection\n",
"# Select specific rows and columns using iloc (integer-location based indexing)\n",
"print(\"Using iloc:\")\n",
"print(df.iloc[2, 2]) # Value at 3rd row, 3rd column\n",
"\n",
"# Select rows using loc (label-based indexing)\n",
"print(\"\\nUsing loc:\")\n",
"display(df.loc[3]) # 4th row\n",
"display(df.loc[0:3]) # First 4 rows\n",
"\n",
"# Query the DataFrame by condition\n",
"print(\"\\nUsing query:\")\n",
"display(df.query(\"year > 2008\"))\n",
"\n",
"# Query dataframe based on two conditions\n",
"\n",
"# Method 1\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 1 Dataframe:\")\n",
"yr_vec = df['year'] > 2008\n",
"island_vec = df['island'] == 'Biscoe'\n",
"\n",
"combine_vec = np.logical_and(yr_vec,island_vec)\n",
"display(df[combine_vec])\n",
"\n",
"#Method 2\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 2 Dataframe:\")\n",
"display(df[(yr_vec) & (island_vec)])"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercises 2\n",
"\n",
"display(iris.head())\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Get out the sepal_length column as a pandas series and rename the series\n",
"print(\"Sepal_length column (as Series):\")\n",
"sepal_length_series = iris['sepal_length']\n",
"display(sepal_length_series)\n",
"\n",
"print(\"\\nSeries name:\")\n",
"print(sepal_length_series.name)\n",
"\n",
"sepal_length_series.name = \"Sepal Length\"\n",
"print(\"\\nUpdated Series name:\")\n",
"print(sepal_length_series.name)\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Get the 5th row, 2nd column element using the iloc function\n",
"\n",
"element_5_2 = iris.iloc[4, 1]\n",
"print(f\"\\n5th row, 2nd column element: {element_5_2}\")\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Get the last 5 rows using the loc function and then iloc\n",
"num_rows = iris.shape[0]\n",
"print(\"\\nUsing loc function:\")\n",
"display(iris.loc[num_rows-5:num_rows-1]) \n",
"print(\"\\nUsing iloc function:\")\n",
"display(iris.iloc[-5:])\n",
"#Note: The iloc function allows for integer-based indexing, which includes using negative indices to count from the end of the DataFrame\n",
"\n",
"# 4. Visualize the distribution of the sepal length of the iris dataset\n",
"plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))\n",
"sns.histplot(iris['sepal_length'], kde=True, bins=20)\n",
"plt.title('Distribution of Sepal Length')\n",
"plt.xlabel('Sepal Length')\n",
"plt.ylabel('Count')\n",
"plt.show()\n",
"\n",
"# 5. Display only the rows that have a petal length greater than or equal to 1.5 and petal width greater than or equal to 0.5\n",
"\n",
"# Method 1\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 1 Dataframe And Logic:\")\n",
"petal_length_bool = iris['petal_length'] >= 1.5\n",
"petal_width_bool = iris['petal_width'] >= 0.5\n",
"\n",
"combine_bool = np.logical_and(petal_length_bool,petal_width_bool)\n",
"display(iris[combine_bool])\n",
"\n",
"#Method 2\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 2 Dataframe And Logic:\")\n",
"display(iris[(petal_length_bool) & (petal_width_bool)])\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"# 6. Display only the rows that meet either of two conditions\n",
"\n",
"# Method 1\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 1 Dataframe Or Logic:\")\n",
"combine_bool = np.logical_or(petal_length_bool,petal_width_bool)\n",
"display(iris[combine_bool])\n",
"\n",
"#Method 2\n",
"print(\"\\nMethod 2 Dataframe Or Logic:\")\n",
"display(iris[(petal_length_bool) | (petal_width_bool)])\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Histograms allowed us to visualize the distribution of a singel feature, what about the relation between features? How do we decide our filtering condition with multiple features?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Create jointplots to determine relationships between specific variables\n",
"sns.jointplot(data=df, x=\"bill_length_mm\", y=\"bill_depth_mm\")\n",
"plt.show()\n",
"\n",
"sns.jointplot(data=df, x=\"body_mass_g\", y=\"flipper_length_mm\")\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Create pairplots to determine relationships between all numeric variables\n",
"sns.pairplot(df)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Different ways of visualizing the same data can lead to different interpretations\n",
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
"fig , ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(15,12), ncols=2,nrows=2)\n",
"sns.swarmplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[0,0],hue='species')\n",
"sns.violinplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[0,1])\n",
"sns.boxplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[1,0])\n",
"sns.barplot(data=df,x='species',y='body_mass_g',ax=ax[1,1])\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercise 3\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Plot relation petal length and petal width\n",
"print('Joint plot of petal length and petal width')\n",
"sns.jointplot(data=iris, x=\"petal_length\", y=\"petal_width\")\n",
"plt.show()\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Plot relationship between all numeric values\n",
"print('\\nPairplot of all numercic values')\n",
"sns.pairplot(iris)\n",
"plt.show()\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Use two different plots to visualize the data for petal length for only the setosa and virginica species\n",
"print('\\nTwo different plots to visualize petal length for only the setosa and virginica species')\n",
"iris_subset = iris[(iris['species'] == 'setosa') | (iris['species'] == 'virginica')]\n",
"fig , ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12,7), ncols=2,nrows=1)\n",
"sns.violinplot(data=iris_subset,x='species',y='petal_length',ax=ax[0])\n",
"sns.barplot(data=iris_subset,x='species',y='petal_length',ax=ax[1])\n",
"plt.show()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### After editing our dataframes how can we save them in a way that allows us to read them back in without having to redo our analysis?"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Saving Pandas Dataframes\n",
"\n",
"df.to_csv('penguins.csv', index=False)\n",
"\n",
"df.to_excel('penguins.xlsx', index=False, sheet_name='Sheet1')"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Reading Pandas Dataframes\n",
"\n",
"df_csv = pd.read_csv('penguins.csv')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from CSV:\")\n",
"display(df_csv)\n",
"\n",
"df_excel = pd.read_excel('penguins.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet1')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from Excel:\")\n",
"display(df_excel)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Excercise 4\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Write the iris dataset to a csv\n",
"iris.to_csv('iris.csv', index=False)\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Write the iris dataset to a excel\n",
"iris.to_excel('iris.xlsx', index=False, sheet_name='Sheet1')\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Read in the iris dataset from the csv\n",
"iris_csv = pd.read_csv('iris.csv')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from CSV:\")\n",
"display(iris_csv)\n",
"\n",
"# 4. Read in the iris dataset from the excel\n",
"iris_excel = pd.read_excel('iris.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet1')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from Excel:\")\n",
"display(iris_excel)\n",
"\n",
"# 5. Write to a file w semicolon as a seperator\n",
"iris.to_csv('iris_semicolon.csv', index=False, sep=';')\n",
"\n",
"# 6. Read in the semicolon file\n",
"iris_semicolon_csv = pd.read_csv('iris_semicolon.csv', sep=';')\n",
"print(\"DataFrame read from semicolon CSV:\")\n",
"display(iris_semicolon_csv)\n"
]
}
],
"metadata": {
"kernelspec": {
"display_name": "Python 3 (ipykernel)",
"language": "python",
"name": "python3"
},
"language_info": {
"codemirror_mode": {
"name": "ipython",
"version": 3
},
"file_extension": ".py",
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
"name": "python",
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
"version": "3.9.-1"
}
},
"nbformat": 4,
"nbformat_minor": 4
}